Table 2.
Pharmacogenetics of lipid-modifying agents.
| Lipid-Modifying Agents | ||
|---|---|---|
| Drug | Properties | Pharmacogenetics |
|
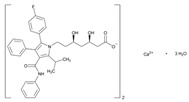
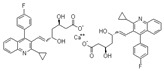
Name: ATORVASTATIN IUPAC Name: 1H-Pyrrole-1-heptanoic acid, 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-β,δ-dihydroxy-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-[(phenylamino)carbonyl]-, calcium salt (2:1), [R-(R*,R*)]-; calcium (βR,δR)-2-(p-fluorophenyl)-β,δ-dihydroxy-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)pyrrole-1-heptanoate (1:2) Molecular Formula: C66H68CaF2N4O10 Molecular Weight: 1155.34 Mechanism: Inhibits 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, resulting in a compensatory increase in the expression of LDL receptors on hepatocyte membranes and a stimulation of LDL catabolism. Effect: Treatment of dyslipidemias or primary prevention of cardiovascular disease (atherosclerotic). |
Mechanistic genes: APOA5, APOB, APOC3, ACE1, APOA1, APOE, CETP, CRP, ESR1, FGB, GNB3, HTR3B, ITGB3, LDLR, LIPC, MMP3, MTTP, NOS3, PON1, USP5 Metabolic genes Substrate: CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP7A1, CYP11B2, UGT1A1, UGT1A3 Inhibitor: ABCB1, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, HMGCR Inducer: CYP2B6 Transporter genes: ABCA1, ABCB1, ABCB11, ABCC1, ABCC2, ABCC3, ABCG2, SLC16As, SLCO1B1, SLCO1B3 Pleiotropic genes: IL6, IL10, TNF |
|
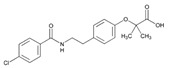
Name: BEZAFIBRATE IUPAC Name: Propanoic acid, 2-[4-[2-[(4-chlorobenzoyl)amino]ethyl]phenoxy]-2-methyl-; 2-[p-[2-(p-chlorobenzamido)ethyl]phenoxy]-2-methylpropionic acid Molecular Formula: C19H20ClNO4 Molecular Weight: 361.82 Mechanism: Mechanism not established. May increase VLDL catabolism by increasing lipoprotein and hepatic triglyceride lipase activities. May decrease triglyceride biosynthesis by inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. May decrease cholesterol biosynthesis by inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methyglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Effect: Adjunct to diet and other therapeutic measures for treatment of type IIa and IIb mixed hyperlipidemia, to regulate lipid and apoprotein levels (reduce serum triglycerides, LDL-C and apolipoprotein B, increase HDL-C and apolipoprotein A). Treatment of adult patients with high to very high triglyceride levels (hypertriglyceridemia)(Fredrickson classification type IV and V hyperlipidemias) who are at high risk of complications from their dyslipidemia. |
Mechanistic genes:ACSL1, ACOX1, APOA5, APOB, APOC3, APOE, CETP, LDLR, LIPC, MGMT, PPARA, SCARB1 Metabolic genes Substrate:CYP1A1, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP7A1, UGT1A1 Inhibitor:ACACA, CYP2C8, HMGCR Inducer:CYP3A4, CYP3A5, UGT1A1 Transporter genes:ABCB11 |
|
Name: COLESTIPOL IUPAC Name: Colestipol hydrochloride; copolymer of diethylenetriamine and 1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane, hydrochloride Molecular Formula: N.A. Molecular Weight: N.A. Mechanism: Binds to bile acids in the intestine and forms a non-absorbable complex. Thus, bile acids are partially removed from enterohepatic circulation and conversion of cholesterol to bile acids in the liver is increased. This enhanced demand for cholesterol in liver cells causes a compensatory increase in hepatic uptake (and thus systemic clearance) of circulating LDL-C. Serum triglyceride concentrations may remain unchanged or increase slightly (5–10%). Antilipemic effects are additive when used with lovastatin or niacin. Effect: Primary hypercholesterolemia. Arteriolosclerosis. Pruritus associated with elevated levels of bile acids. To decrease plasma half-life of digoxin in toxicity. |
Mechanistic genes:APOE, LIPC Metabolic genes Substrate:CYP7A1 |
|
|
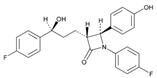
Name: EZETIMIBE IUPAC Name: 2-Azetidinone, 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]-4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-, [3R-[3α(S*),4β]]-; (2)(3R,4S)-1-(p-fluorophenyl)-3-[(3S)-3-(p-fluorophenyl)-3-hydroxypropyl]-4-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-azetidinone Molecular Formula: C24H21F2NO3 Molecular Weight: 409.43 Mechanism: Inhibits absorption of cholesterol at the brush border of the small intestine via the sterol transporter, Niemann–Pick C1-Like 1 (NPC1L1). This leads to a decreased delivery of cholesterol to the liver, reduction in hepatic cholesterol stores and increased clearance of cholesterol from the blood. Decreases total cholesterol, LDL-C, APOB, and triglycerides while increasing HDL-C. Effect: Used in combination with dietary therapy for treatment of primary hypercholesterolemia (as monotherapy or in combination with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors). Homozygous sitosterolemia. Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (in combination with atorvastatin or simvastatin). Mixed hyperlipidemia (in combination with fenofibrate). |
Mechanistic genes:APOE, APOA1, APOA5, APOB, APOC3, CETP, NPC1, NPC1L1, SCARB1 Metabolic genes Substrate:CYP7A1, UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT2B7, UGT2B15 Transporter genes:ABCB1, ABCA1, ABCC2, SLCO1B1, SLCO1B3 |
|
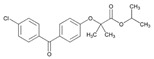
Name: FENOFIBRATE IUPAC Name: Isopropyl 2-[p-(p-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropionate Molecular Formula: C20H21ClO4 Molecular Weight: 360.83 Mechanism: Fenofibric acid is believed to increase VLDL catabolism by enhancing the synthesis of lipoprotein lipase. As a result of a decrease in VLDL levels, total plasma triglycerides are reduced by 30%–60%. Modest increase in HDL occurs in some hypertriglyceridemic patients. Effect: Adjunct to dietary therapy to decrease elevated serum total and LDL-C, triglyceride, and apolipoprotein B (APOB) concentrations, and to increase HDL-C concentrations in the management of primary hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia, including heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and other causes of hypercholesterolemia. Additive antilipemic effects when used concomitantly with other antilipemic agents (e.g., colesevelam and ezetimibe). Adjunct to dietary therapy in management of hypertriglyceridemia. |
Mechanistic genes:ACE1, ACOX1, APOA1, APOA5, APOB, APOE, FABP1, FABP2, LPL, PPARA, SCARB1 Metabolic genes Substrate:CYP2C8, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, UGT1A1 Inhibitor:CYP2A6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP4F2 Inducer:CYP2C8, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, UGT1A1 Transporter genes:ABCA1, ABCB1 Pleiotropic genes:APP, IL6 |
|
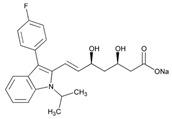
Name: FLUVASTATIN IUPAC Name: 6-Heptenoic acid, 7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-methylethyl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-, monosodium salt, [R*,S*-(E)]-(±)-; sodium (±)-(3R*,5S*,6E)-7-[3-(p-fluorophenyl)-1-isopropylindol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoate Molecular Formula: C24H25FNNaO4 Molecular Weight: 433.45 Mechanism: Acts by competitively inhibiting 3-hydroxyl-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase (HMGCR), the enzyme that catalyzes reduction in HMG-CoA to mevalonate. HDL is increased while total, LDL and VLDL cholesterols, apolipoprotein B, and plasma triglycerides are decreased. Effect: Used as a component of multiple risk factor intervention in patients at risk for atherosclerosis vascular disease due to hypercholesterolemia. |
Mechanistic genes:ACE1, APOA1, APOA5, APOB, APOC3, APOE, CETP, LDLR, LIPC, LPL, NOS3, NR1I2, NR1I3, PPARD, PON1, USP5 Metabolic genes Substrate:CYP1A1, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP7A1, UGT1A3 Inhibitor:CYP1A2, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, HMGCR Transporter genes:ABCA1, ABCB1, ABCB11, ABCC2, ABCG2, SLC15A1, SLC22A8, SLCO1B1, SLCO1B3, SLCO2B1 |
|
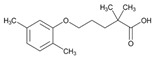
Name: GEMFIBROZIL IUPAC Name: Pentanoic acid, 5-(2,5-dimethylphenoxy)-2,2-dimethyl-; 2,2-dimethyl-5-(2,5-xylyloxy)valeric acid Molecular Formula: C15H22O3 Molecular Weight: 250.33 Mechanism: Gemfibrozil can inhibit lipolysis and decrease subsequent hepatic fatty acid uptake as well as inhibit hepatic secretion of VLDL. Together, these actions decrease serum VLDL levels. Increases HDL-C. Effect: Gemfibrozil is used to reduce risk of developing coronary heart disease (CHD) in patients with type IIb hyperlipoproteinemia without clinical evidence of CHD (primary prevention) who have inadequate response to dietary management, weight loss, exercise, and drugs known to reduce LDL-C and increase HDL-C and who have low HDL-C concentrations in addition to elevated LDL-C and triglycerides. In addition, gemfibrozil is used for treatment of hypertriglyceridemia in types IV and V hyperlipidemia for patients at greater risk for pancreatitis and who have not responded to dietary intervention. |
Mechanistic genes:ACE1, ACOX1, AHR, APOE, CES2, CETP, CFTR, LPL, MMP3, NR1I2, PPARA, SCARB1 Metabolic genes Substrate:CYP2D6, CYP2C8, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP7A1, UGT1A1, UGT1A3 Inhibitor:CYP1A2, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A4, CYP3A5 Inducer:CYP2C8, UGT1A1 Transporter genes:ABCB1, SLCO1B1, SLCO1B2 Pleiotropic genes:IL1B, IL12B, TNF |
|
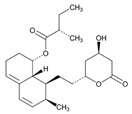
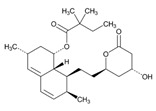
Name: LOVASTATIN IUPAC Name: Butanoic acid, 2-methyl-, 1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-(tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl]-1-naphthalenyl ester, [1S-[1α(R*),3α,7β,8β(2S*,4S*),8aβ]]-; (S)-2-methylbutyric acid, 8-ester with (4R,6R)-6-[2-[(1S,2S,6R,8S,8aR)-1,2,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-8-hydroxy-2,6-dimethyl-1-naphthyl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-2H-pyran-2-one Molecular Formula: C24H36O5 Molecular Weight: 404.54 Mechanism: Acts by competitively inhibiting 3-hydroxyl-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, enzyme which catalyzes rate-limiting step in cholesterol biosynthesis. Effect: Adjunct to dietary therapy to decrease elevated serum total and LDL-C concentrations in primary hypercholesterolemia. Primary prevention of coronary artery disease (patients without symptomatic disease with average to moderately elevated total and LDL-C and below average HDL-C). Slow progression of coronary atherosclerosis in coronary heart disease. Adjunct to dietary therapy in adolescent patients (10–17 years of age, females >1 year postmenarche) with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia having LDL>189 mg/dL, or LDL>160 mg/dL with positive family history of premature cardiovascular disease, or LDL>160 mg/dL with presence of at least two other CVD risk factors. |
Mechanistic genes:APOA1, APOA5, APOB, APOC3, CETP, KCNH2, LDLR, LIPC, LPL, USP5 Metabolic genes Substrate:CYP2C8, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, UGT1A3 Inhibitor:ABCB1, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, HMGCR Inducer:CYP2B6, CYP7A1 Transporter genes:ABCA1, ABCB1, ABCB11, ABCC2, ABCG2, SLCO1B1, SLCO1B3 Pleiotropic genes:TP53 |
|
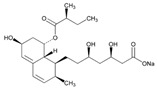
Name: PITAVASTATIN IUPAC Name: Calcium (E,3R,5S)-7-[2-cyclopropyl-4-(4-fluorophenyl)quinolin-3-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoate; (+)monocalcium bis{(3R, 5S, 6E)-7-[2-cyclopropyl-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-quinolyl]-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoate} Molecular Formula: C50H46CaF2N2O8 Molecular Weight: 880.98 Mechanism: Pitavastatin competitively inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, which is a rate-determining enzyme involved with biosynthesis of cholesterol, in a manner of competition with the substrate so that it inhibits cholesterol synthesis in the liver. As a result, the expression of LDL receptors followed by the uptake of LDL from blood to liver is accelerated and then the plasma total cholesterol (TC) decreases. Furthermore, sustained inhibition of cholesterol synthesis in the liver decreases levels of very low-density lipoproteins. Effect: Adjunct to dietary therapy to reduce elevations in TC, LDL-C, apolipoprotein B (Apo B), and triglycerides (TG), and to increase low HDL-C in patients with primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia. |
Metabolic genes Substrate:CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, UGT1A3, UGT2B7 Inhibitor:HMGCR Transporter genes:ABCB1, ABCG2, SLCO1B1 |
|
Name: PRAVASTATIN IUPAC Name: 1-Naphthaleneheptanoic acid, 1,2,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-β,δ,6-trihydroxy-2-methyl-8-(2-methyl-1-oxobutoxy)-, monosodium salt, [1S-[1α(βS*,δS*),2α,6α,8β(R*),8aα]]-; sodium (+)-(βR,δR,1S,2S,6S,8S,8aR)-1,2,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-β,δ,6,8-tetrahydroxy-2-methyl-1-naphthaleneheptanoate, 8-[(2S)-2-methylbutyrate] Molecular Formula: C23H35NaO7 Molecular Weight: 446.51 Mechanism: A competitive inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. Effect: Primary prevention of coronary events (reduction in cardiovascular morbidity (myocardial infarction, coronary revascularization procedures) and mortality). Secondary prevention of cardiovascular events in established coronary heart disease (slowing of progression of coronary atherosclerosis, reduction in cardiovascular morbidity (myocardial infarction, coronary vascular procedures) and reduction in mortality, reduction in risk of stroke and transient ischemic attacks). Hyperlipidemias (reduction in elevations in total cholesterol, LDL-C, apolipoprotein B, and triglycerides). Heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. |
Mechanistic genes:ACE1, ALDH1A1, APOA1, APOA5, APOB, APOC3, APOE, CBS, CETP, CRP, FGB, HMGCR, HTR3B, ITGB3, LDLR, LEP, LIPC, LPL, MMP2, MMP3, MTHFR, NOS3, PON1, USP5 Metabolic genes Substrate:CYP1A1, CYP1A2, CYP2C8, CYP2E1, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP7A1, UGT1A3 Inhibitor:ABCB1, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, HMGCR Inducer:CYP2B6 Transporter genes:ABCA1, ABCB1, ABCB11, ABCC2, ABCG2, SLC22A8, SLCO1A2, SLCO1B1, SLCO1B3, SLCO2B1 Pleiotropic genes:IL1B, IL6, IL10, TP53 |
|
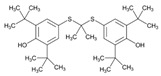
Name: PROBUCOL IUPAC Name: Phenol, 4,4′-[(1-methylethylidene)bis(thio)]bis[2,6-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-; acetone bis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) mercaptole Molecular Formula: C31H48O2S2 Molecular Weight: 516.84 Mechanism: Increases fecal loss of bile acid-bound low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, decreases synthesis of cholesterol and inhibits enteral cholesterol absorption. Effect: Adjunct to dietary therapy to decrease elevated serum total and LDL-C concentrations in primary hypercholesterolemia. |
Mechanistic genes:APOB, APOC3, KCNH2, SCARB1 Metabolic genes Substrate:CYP2D6, CYP3A4, CYP3A5 Pleiotropic genes:TNF |
|
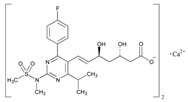
Name: ROSUVASTATIN IUPAC Name: 6-Heptenoic acid, 7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-(1-methylethyl)-2-[methyl(methylsulfonyl)amino]-5-pyrimidinyl]-3,5-dihydroxy-, calcium salt (2:1), (3R,5S,6E)-; [S-[R*,S*-(E)]]-7-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-6-(1-methylethyl)-2-[methyl(methylsulfonyl)amino]-5-pyrimidinyl]-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoic acid, calcium salt (2:1) Molecular Formula: [C22H27FN3O6S]2Ca Molecular Weight: 1001.14 Mechanism: Inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol synthesis. This results in compensatory increase in expression of LDL receptors on hepatocyte membranes and stimulation of LDL catabolism. Effect: Used with dietary therapy for hyperlipidemias to reduce elevations in total cholesterol (TC), LDL-C, apolipoprotein B, non-HDL-C, and triglycerides in primary hypercholesterolemia (elevations of 1 or more components present in Fredrickson type IIa, IIb, and IV hyperlipidemias). Treatment of primary dysbetalipoproteinemia (Fredrickson type III hyperlipidemia). Treatment of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. To slow progression of atherosclerosis as adjunct to TC- and LDL-C-lowering diet. |
Mechanistic genes:ACE1, APOA1, APOA5, APOB, APOC3, APOE, CETP, FGB, ITGB3, LDLR, LIPC, LPL, NOS3, TCF20, USP5 Metabolic genes Substrate:CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP7A1, UGT1A3 Inhibitor:CETP, HMGCR, SLCO1B1 Inducer:CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP3A4, CYP3A5 Transporter genes:ABCA1, ABCB1, ABCB11, ABCC1, ABCC4, ABCG2, SLC10A1, SLCO1A2, SLCO1B1, SLCO1B3, SLCO2B1, SLC22A8 |
|
Name: SIMVASTATIN IUPAC Name: Butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-, 1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-(tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl]-1-naphthalenyl ester, [1S-[1α,3α,7β,8β(2S*,4S*),8aβ]]-; 2,2-dimethylbutyric acid, 8-ester with (4R,6R)-6-[2-[(1S,2S,6R,8S,8aR)-1,2,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-8-hydroxy-2,6-dimethyl-1-naphthyl]ethyl]tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-2H-pyran-2-one Molecular Formula: C25H38O5 Molecular Weight: 418.57 Mechanism: Prodrug requiring hydrolysis in vivo for activity. Inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, causing subsequent reduction in hepatic cholesterol synthesis. Reduces serum concentrations of total cholesterol, LDL-C, Apo B, and triglycerides. Statins may slow progression and/or induce regression of atherosclerosis in coronary and/or carotid arteries, modulate blood pressure in hypercholesterolemic patients with hypertension, and possess anti-inflammatory activity. Effect: Secondary prevention of cardiovascular events in hypercholesterolemic patients with established coronary heart disease or at high risk for coronary heart disease. Hyperlipidemias (primary hypercholesterolemia, homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia). |
Mechanistic genes:APOA1, APOA5, APOB, APOC3, APOE, CETP, F2, FGB, GNB3, HMGCR, HTR3B, LDLR, LIPC, LPL, NOS3, PRNP, USP5, VCAM1 Metabolic genes Substrate:CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP7A1, POR, UGT1A3 Inhibitor:CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, HMGCR Inducer:CYP2B6 Transporter genes:ABCA1, ABCB1, ABCB11, ABCC2, ABCC3, ABCG2, SLCO1B1, SLCO1B3 Pleiotropic genes:IL6, TNF |
