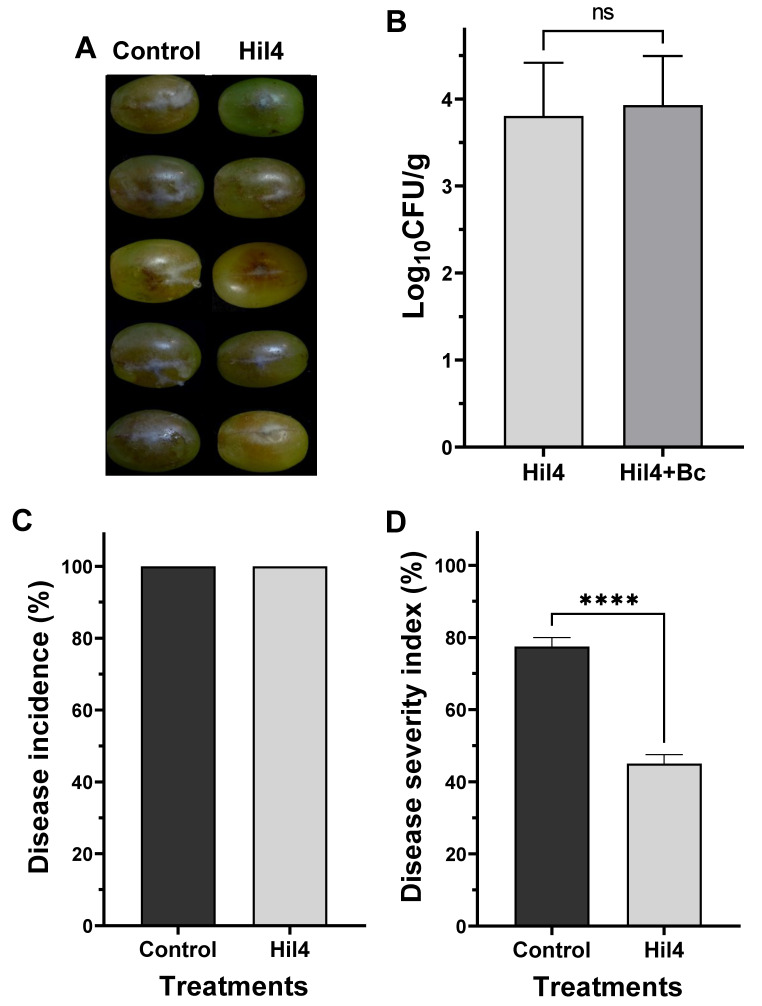
Figure 8.
Efficacy of Hil4 culture in controlling gray mold disease of grape berries caused by B. cinerea in a preventive application. Artificial wounds on grape berries were inoculated with 5 μL of bacterial culture (108 CFU/mL) and incubated for 36 h in the dark at 25 °C. Then, 5 μL of B. cinerea spores (105 spores/mL) were inoculated in the same wound and fruit were further incubated for 3 days. Control treatment consisted of the pathogen inoculated alone. (A) Representative images of grape berries; (B) population dynamics of Hil4 in the wound tissue of grape berries (Log10CFU/g) pooled from 3 independent experiments each consisting of 6 berries (n = 18)d (C) disease incidence calculated as the percentage of infected fruit in 3 independent experiments each consisting of 10 berries (n = 3); (D) disease severity index (%), calculated in 3 independent experiments each consisting of 10 berries (n = 3) using a formula. Data represent mean (SD) values and asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between untreated control and treated with Hil4 after t test analysis (ns, non-significant; ****, p < 0.0001).