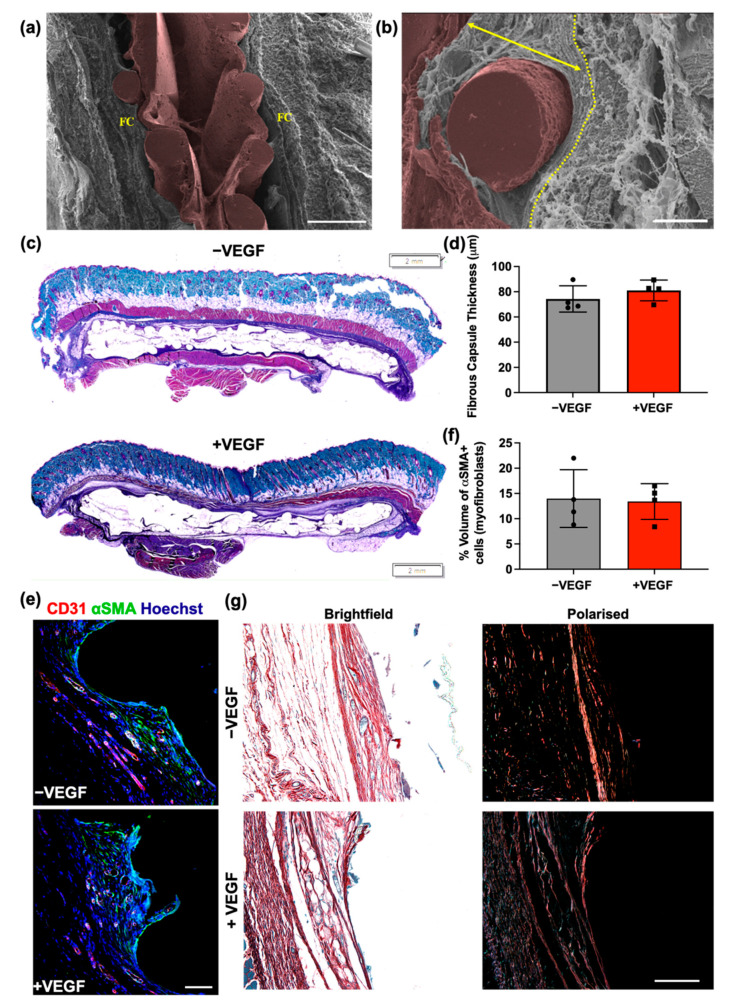
Figure 4.
VEGF does not affect the structure and composition of the fibrous capsule. (a) Overview of encapsulation device (pseudo-coloured in brown) in-situ with surrounding fibrous capsule (FC). Scale bar = 500 μm. (b) Fibrous capsule surrounding rope coil on external surface of +VEGF device. Yellow dotted line marks outer boundary of the fibrous capsule before muscle layer. Arrow demonstrates where an FC measurement would have been taken, perpendicular to the tissue–device interface. Scale bar = 100 μm. (c) Representative Masson’s trichrome-stained histological sections of −VEGF and +VEGF groups. Scale bar = 2 mm. (d) Mean fibrous capsule thicknesses. (e) Representative immunofluorescent images of myofibroblasts within the surrounding fibrous capsule (Hoechst, blue; αSMA, green; CD31, red). (f) Percentage volume of αSMA+ cells (myofibroblasts) within the fibrous capsule. (g) Representative polarised light microscopy images for analysis of the fibrous capsule and collagen maturity at the tissue–device interface. Scale bar = 100 μm. (Red/Orange = mature collagen; Green/Yellow = immature collagen). n = 4 per group, data are represented as means ± SD.