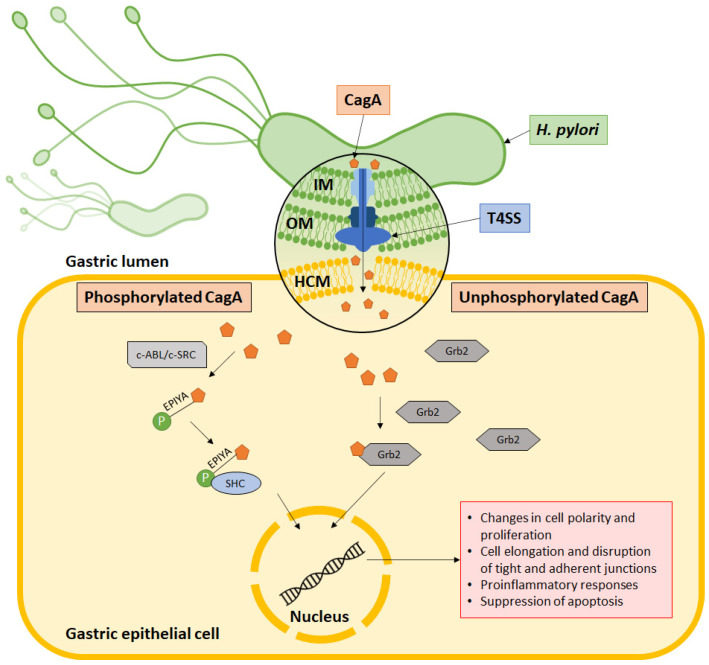
Figure 2.
CagA’s mechanism of action. CagA is injected into the host cell via the type IV secretion system (T4SS), which is made up of an outer membrane ring occupying the outer membrane (OM), an inner membrane ring at the inner membrane (IM) and a pilus to inject CagA across the host cell membrane (HCM) into the cytoplasm. Some CagA undergo phosphorylation at the EPIYA motif via c-ABL or c-SRC and associates with the SHC domain to induce pathologies. Meanwhile, some CagA associate with Grb2 to induce pathology without undergoing phosphorylation.