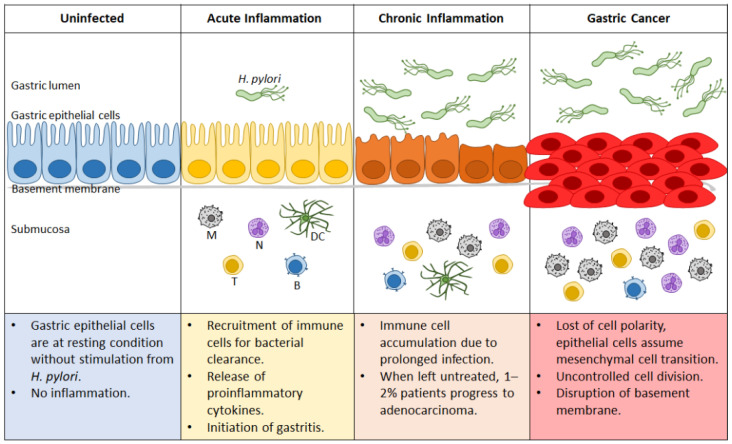
Figure 3.
Progression of gastric cancer during Helicobacter pylori infection. Uninfected gastric epithelial cells are healthy, with no sign of inflammation. Upon H. pylori infection, acute inflammation ensues that can progress to gastritis. Ineffective bacterial clearance leads to prolonged infection and continuous recruitment of immune cells, resulting in chronic inflammation. Depending on genetic and environmental factors, approximately 1–2% of the afflicted patients progress to gastric cancer. N: neutrophil; M: macrophage; DC: dendritic cell; T: T cell; B: B cell.