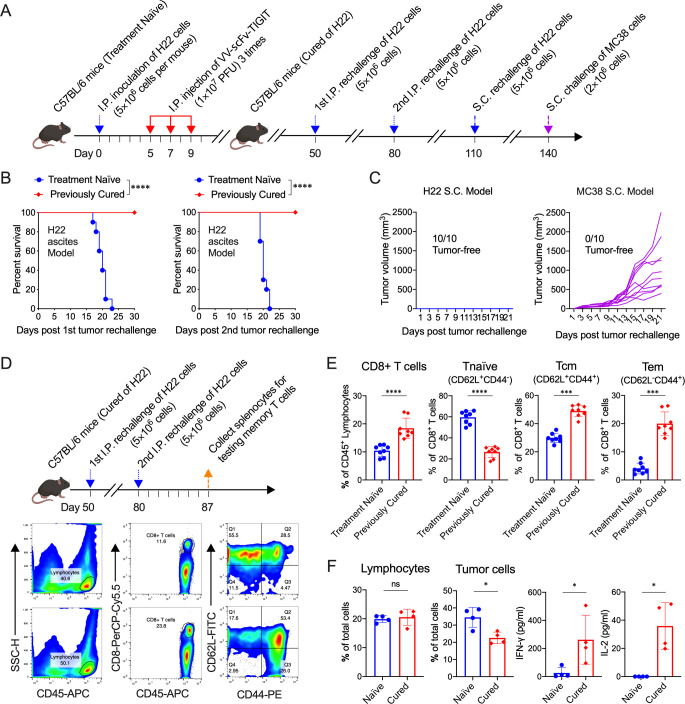
Figure 6.
Treatment of mice with VV-scFv-TIGIT established long-term tumor-specific immunological memory. (A) Rechallenge scheme. (B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of the treatment-naïve mice or the mice cured of H22 by VV-scFv-TIGIT. (C) Tumor volumes of previously cured mice rechallenged with H22 or MC38 cells subcutaneously. (D) Rechallenge scheme and representative diagram of flow cytometric analysis of memory T cells. (E) Flow cytometric analysis of the proportion of CD8+ T cells, naïve (CD62L+CD44−), effector memory (CD62L-CD44+) and central memory (CD62L+CD44+) CD8+ T cells. (F) Co-culture of H22 cells with splenocytes from the H22 rechallenged mice. The proportion of lymphocytes and tumor cells in the co-culture system was detected by flow cytometry. The levels of cytokines in the co-culture system were detected by ELISA. ns, no significant differences; *p<0.05; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001. scFv, single-chain variable fragment; TIGIT, T-cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain; VV, vaccinia virus.