Table 2.
Monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes present in Lamiaceae with biological activity and their molecular targets explored in pain and inflammation.
| Compound | Structure | Mechanism of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
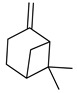
| β-pinene |
|
Decreased expression of IL-6, TNF-α, NO, iNOS and COX-2. Down-regulation of MAPKs phosphorylation and the NF-κB signaling pathway |
[127] |
| Inhibition of COX-2 enzyme expression | [128] | ||
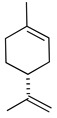
| Limonene |
|
Reduction in leukocyte infiltration and TNF-α levels. | [129] |
| Decreased production of NO, PGE2 and Pro-inflammatory cytokines | [130] | ||
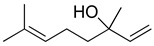
| Linalool |
|
Inhibition of pro-inflammatory interleukins and modulation of NMDA glutamatergic receptor. | [131] |
| Reduction in oxidative stress and inflammation (NF-kB). | [132] | ||
| Activation of opioid and muscarinic receptors | [133] | ||
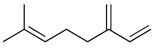
| Myrcene |
|
Activation of opioid receptors and presynaptic α2 adrenoreceptor. | [134] |
| Inhibition of IL-1β-induced NO production Increased expression of TIMP-1 and TIMP-3. |
[135] | ||
| p-cymene |
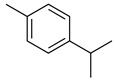
|
Reduced the production of pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α, the migration of leukocytes, and the release of NO. Activation of opioid receptors. | [136] |
| Reduced the calcium current density. | [137] | ||
| Thymol |
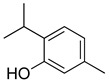
|
Voltage-operated sodium channel blocker | [138] |
| TRPA1 channel presynaptic activation | [139] | ||
| Carvacrol |
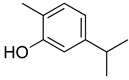
|
Inhibition of expression TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 Reduced the expression of NF-kB |
[140] |
| Modulation of opioid, vanilloid and glutamate systems | [141] | ||
| α-humulene |
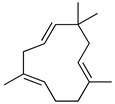
|
Inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-1β) and PGE2 generation. Decreased expression of iNOS and COX-2. Inhibition of Il-5, CCL11 and LTB4 levels and P-selectin expression. |
[142] [143] |
| β-caryophyllene |
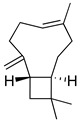
|
Cannabinoid receptor type 2 agonist. Attenuation of Substance P and cytokines such as IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6. |
[144] |
| Agonist to opioid, benzodiazepine, 5HT1A receptors and NO. | [145] |
Abbreviations: COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; IL-: Interleukin-; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; LTB4: Leukotriene B4; MAPKs: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-kB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; NO: Nitric oxide; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; TIMP-: Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TRPA1: Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily A, member 1.
