Table 4.
Phenolic acids commonly found in Lamiaceae and their molecular targets explored in pain and inflammation.
| Compound | Structure | Mechanisms of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rosmarinic acid |
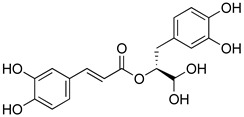
|
Antioxidant activity. | [75] |
| Suppression of TNF-α, iNOs, apoptotic factors (Bax, caspases 3 and 9), Iba-1, TLR4 and GFAP levels. | [181] | ||
| Gallic acid |
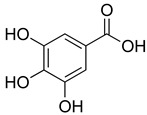
|
ERK-Nrf2-Keap1-mediated antioxidant activity. | [182] |
| Reduction in TBARS, total calcium, TNF-α, superoxide anion, and MPO activity levels; and decreased GSH level. | [183] | ||
| TRPA1 antagonist. | [184] | ||
| Chlorogenic acid |
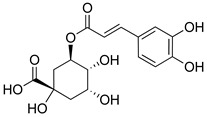
|
Inhibition of CD80/86 and Th1 cytokines. | [185] |
| GABAA receptor agonist. | [186] | ||
| Inhibition of NF-kB and JNK/AP-1 signaling pathways. | [187] | ||
| Vanillin |
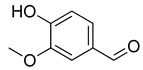
|
Inhibition of protein and lipid oxidation processes. Increased activity of GSH, SOD, catalase.Suppresses the expression of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and plasma AST and ALT enzymes. | [188] |
| α2-adrenergic and opioid receptor agonist | [189] | ||
| Caffeic acid |
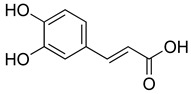
|
Reduction in the IκBα degradation and p65 phosphorylation in the NF-kB pathway. | [190] |
| Inhibition of MPO, MDA and nitrite generation. | [191] | ||
| Vanillic acid |
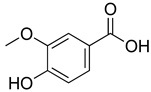
|
α2-adrenoceptor agonist.5HT3 and 5HT1 receptor agonist Interaction with TRPV1, TRPA1 and TRPM8 receptors. | [192] |
| Inhibition of oxidative stress, pro-inflammatory cytokine production, and NF-kB activation. | [193] | ||
| Ferulic acid |
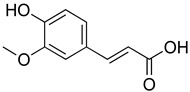
|
The level/activity of elastase, lysosomal enzymes, nitric oxide, lipid peroxidation, and pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-1β); and the mRNA expression of NLRP3 inflammasomes, caspase-1, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and NF-kB p65 were decreased. | [194] |
| Inhibition of xanthine oxidase and COX-2 enzyme. | [195] |
Abbreviations: 5HT: Serotonin; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AP-1: Activator protein 1; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; Bax: Bcl-2-associated X protein; CD80/86: CD28 receptor binds to the B7; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; ERK: Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; GABAA: γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor; GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein; GSH: Glutathione; Iba-1: Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1; IL-: Interleukin-; iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; IkBα: Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; Keap1: Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; MDA: Malondialdehyde; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; mRNA: Messenger Ribonucleic acid; NF-kB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NLRP3: Family pyrin domain containing 3; NRf2: nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2; p65: Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p65 subunit; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; TBARS: Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances; Th1: T helper type 1; TLR4: Toll like receptor 4; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TRPA1: Transient receptor potential ankyrin 1; TRPA1: Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily A, member 1; TRPM8: Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M (melastatin), member 8; TRPV1: Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1.
