Table 5.
Flavonoids commonly present in Lamiaceae and their molecular targets explored in pain and inflammation.
| Compound | Structure | Mechanism of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pedalitin |
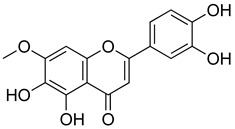
|
Inhibitory effects against NO, TNF-α and IL-12. | [202] |
| Rutin |
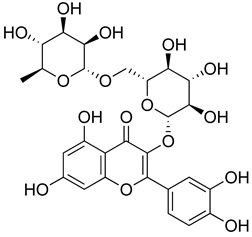
|
Increased activity of GPx, GRd, CAT, SOD and GSH. | [203] |
| Central modulation of the vlPAG descending circuit partly mediated by an opioidergic mechanism. | [106] | ||
| Increased H2S level.Modulation of Nrf2 pathway. Caspase 3 and, NF-kB, TNF-α, IL-6 decreased.Increased sensory nerve conduction velocity. | [204] | ||
| Apigenin |
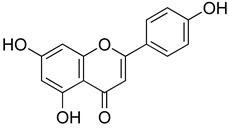
|
Increased expression levels of Nrf2 and HO-1.Inhibition of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, MPO and MDA content. | [24] |
| Inhibition of CD40, TNF-α and IL-6 | [205] | ||
| Quercetin |
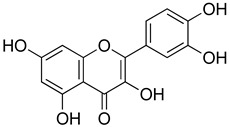
|
Interaction with L-arginine-nitric oxide, serotonin, and GABAergic systems. | [206] |
| ROCs and VOCs Blocker Modulation of PGF2α pathway | [207] | ||
| 5HT1A agonist | [208] | ||
| Luteolin |
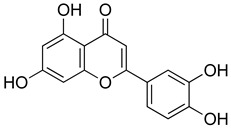
|
Inhibition of IL-1β, TNF-α and histamine release. | [209] |
| Decreased neutrophil infiltration.Inhibition of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6. | [210] | ||
| Downregulation of TLR4/TRAF6/NF-kB pathway | [211] | ||
| Inhibition of CD40, TNF-α and IL-6 | [205] | ||
| Hesperidin |
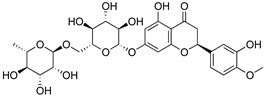
|
Modulation of D2, GABAA and opioid receptors. | [212] |
| Agonist of opioid receptors. | [213] | ||
| Modulation of TRPV1 receptor. | [189] | ||
| Naringin |
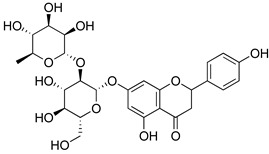
|
Inhibition of oxido-nitrosative strees, TNF-α, IL’s and NF-kB mRNA levels. | [214] |
| Inhibition of PGE2, NO, IL-6 and TNF-α. | [215] | ||
| Naringenin |
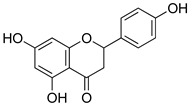
|
Inhibition of NF-kB and activation of NO-Cyclic GMP-PKG-ATP sensitive K+ channel pathway | [216] |
| Inhibition of IL-6, TNF-α and NO release, by interfering MAPK signal pathway and suppressing the activation of NF-kB. | [217] |
Abbreviations: 5HT1A: Serotonin 1A receptor; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; CAT: Catalase; CD40: Cluster of differentiation 40; GABA: γ aminobutyric acid; GMP: Cyclic guanosine monophosphate; GPx: glutathione peroxidase; GRd: glutathione; reductase; GSH: Glutathione; H2S: Hydrogen sulfide; HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1; IL-: Interleukin-; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MDA: Malondialdehyde; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; mRNA: Messenger Ribonucleic acid; NF-kB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NF-kB: Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NO: Nitric oxide; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; PGF2α: Prostaglandin F2α: PKG: cGMP-dependent protein kinase ROCs: Receptor-operated channels; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TRAF6: TNF receptor associated factor 6; TRPV1: Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1; VOCs: Voltage-operated channels.
