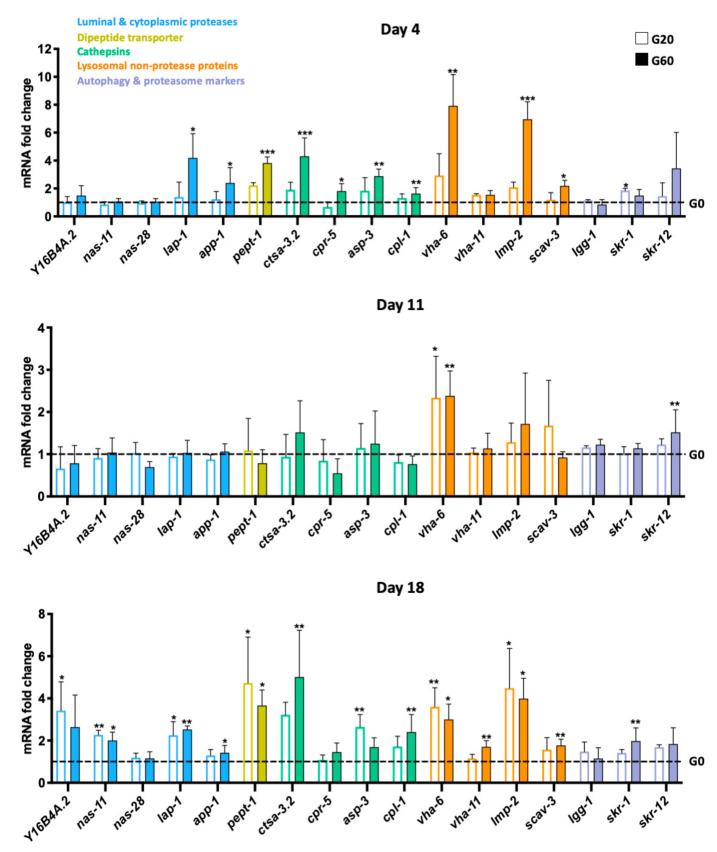
Figure 3.
Impact of dietary Nε-carboxymethyllysine (dCML) exposure on transcriptional regulation of some digestive enzymes, lysosomal proteins and proteasomal and autophagy markers. Young adult worms were fed with bacteria, which were pretreated with 0 mM (G0), 20 mM (G20) or 60 mM (G60) of glyoxylic acid. After 4, 11 and 18 days of culture, relative expression of genes coding for luminal and/or cytoplasmic proteases, cathepsins, lysosomal nonprotease proteins, an autophagy marker and proteasome markers were analyzed by comparing all the conditions to the G0. Data were expressed as means ± standard deviation of 3 biological replicates. The cdc-42 and pmp-3 genes were used to normalize levels of gene expression. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001 G20 or G60 vs. G0 (Kruskal–Wallis, Dunn’s multiple comparisons test).