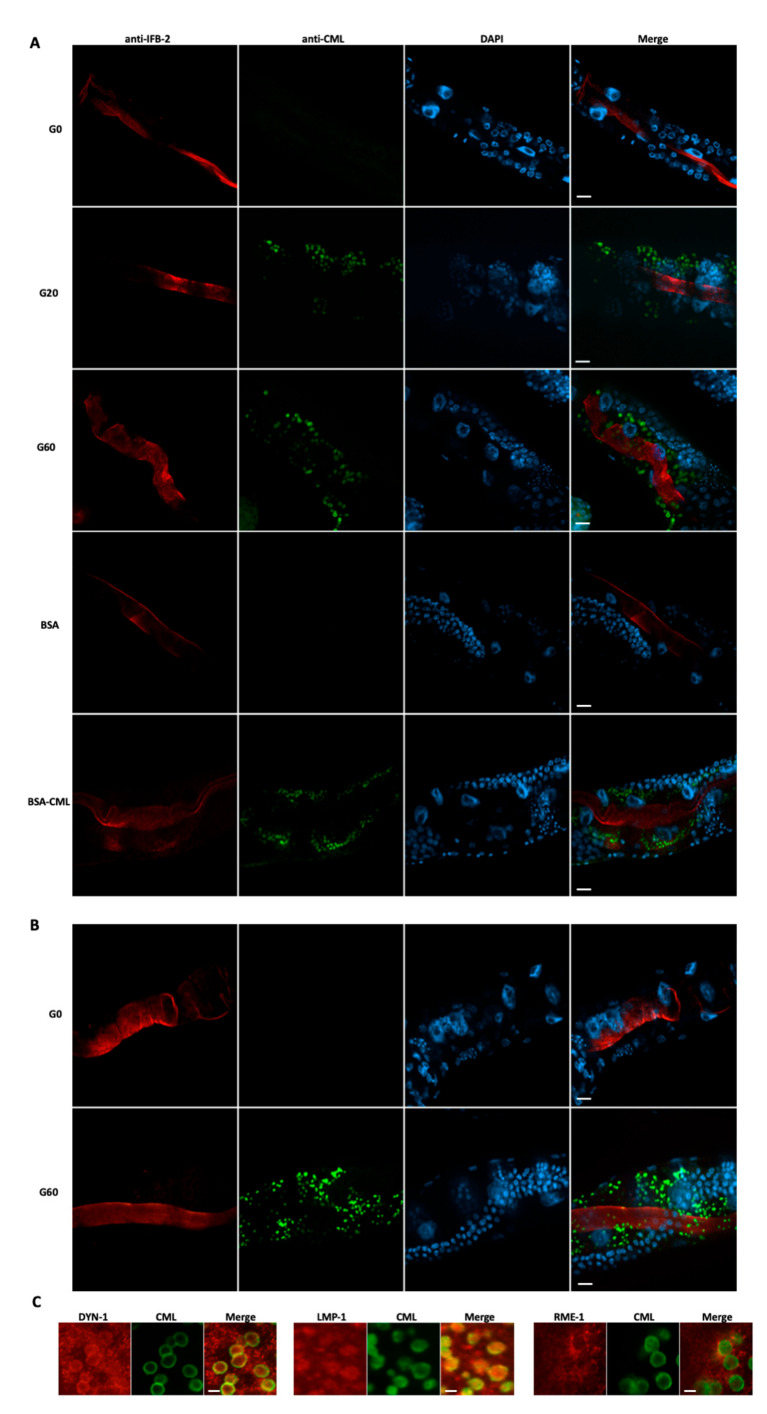
Figure 4.
Mapping of Nε-carboxymethyllysine (CML) epitopes in C. elegans intestine. (A) Immunohistochemical staining was performed on worms fed for 4 days with bacteria, which were pretreated with 0 mM (G0), 20 mM (G20) or 60 mM (G60) of glyoxylic acid, or 1.6 mg/mL of non-glycated bovine serum albumin (BSA) or glycated BSA (BSA-CML), using anti-CML and anti-IFB-2 antibodies. (B) Worms were fed for 4 days with either G0 or G60 bacteria. After washing, worms were incubated for 6 h in nutrient-free buffer, fixed and permeabilized with modified Bouin’s solution and stained with anti-CML and anti-intermediate filament B (IFB-2) antibodies. (C) Immunohistochemical staining was performed on worms fed for 4 days with G60 using either anti-CML and anti-dynamin (DYN-1) antibodies, anti-CML and anti-lysosome-associated membrane protein homolog 1 (LMP-1) antibodies or anti-CML and anti-endocytosis-mediating receptor 1 (RME-1) antibodies. Worms’ nuclei were stained with DAPI. For each type of feeding condition, fluorescence micrographs with the mentioned DNA-binding probe or antibody are shown. Scale bars = 10 μm (A,B) and 2.5 μm (C). All results are representative of 3 independent experiments.