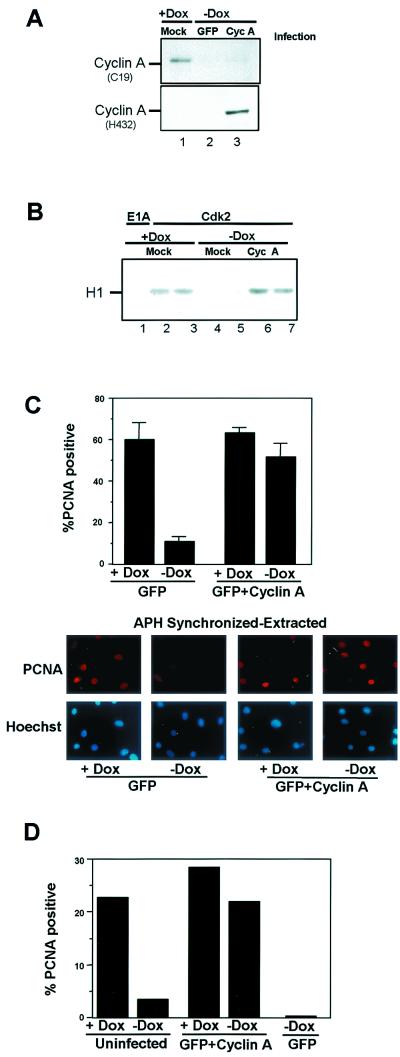
FIG. 7.
Ectopic expression of cyclin A restores PCNA chromatin association. (A) Cells were synchronized in S phase with APH, then cultured in the presence of APH in medium containing Dox (lanes 1) or shifted to APH medium lacking Dox and then immediately infected with adenoviruses encoding GFP or cyclin A-GFP (lanes 2 and 3, respectively). Cells were harvested after 16 h, and total protein was resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with either C-19 or H432 cyclin A antibodies. (B) Cell were synchronized in S phase with APH and then cultured in the presence (lanes 1 to 3) or absence (lanes 4 to 7) of Dox and either mock infected (lanes 1 to 5) or infected with the cyclin A-GFP adenovirus (lanes 6 and 7). CDK2 was immunoprecipitated, and resulting immune complexes were used in in vitro kinase reactions against histone H1 (duplicate experiments are shown). (C) Cells were seeded on coverslips and synchronized in S-phase with APH. These cells were then subsequently cultured with and without Dox (with APH) and infected with adenoviruses bearing GFP or cyclin A-GFP. Soluble proteins were extracted, and cells were fixed and processed for PCNA immunofluorescence. Values shown are the averages of three independent experiments with at least 150 cells counted per experiment. Representative photomicrogaphs taken at ×60 magnification are shown. (D) Asynchronously growing cells were noninfected or infected with adenovirus constructs expressing GFP or cyclin A-GFP. Cells were extracted, fixed, and processed for PCNA immunofluorescence. At least 150 cells were counted in the experiment.