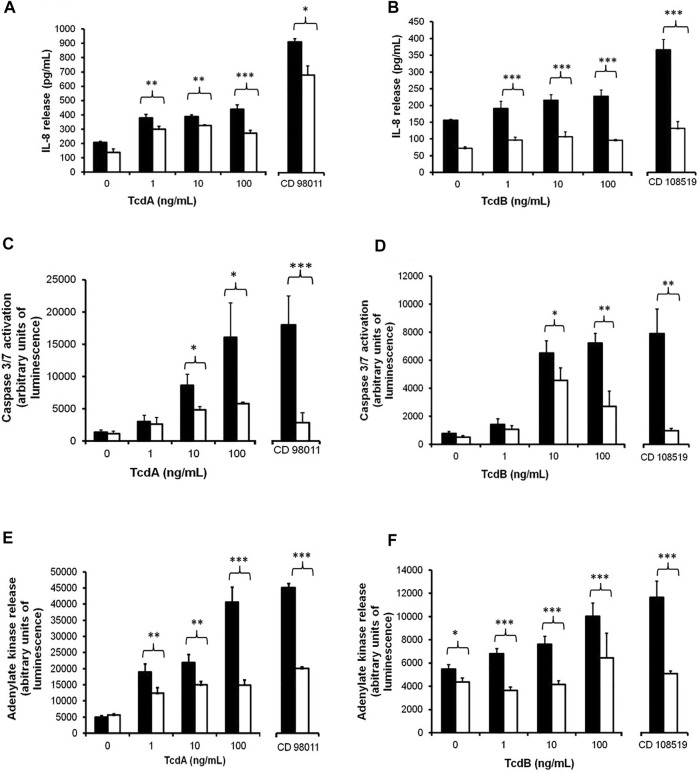
FIGURE 5.
Soluble NSP from plantain reduces C. difficile bacterium and toxin A and toxin B mediated inflammation, cellular apoptosis and cytotoxicity in intestinal epithelial cells. Caco-2 cell monolayers were treated with C. difficile toxins A (TcdA) or toxin B (TcdB), at 1–100 ng/ml for 24 h, in the absence (black bars) or presence of 10 mg/ml plantain NSP (white bars). In parallel, Caco-2 cells were infected with the TcdA+/TcdB+/CDT + C. difficile isolate 98011 or the TcdB + C. difficile isolate 108519, at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 100 for 4 h, again in the absence or presence of plantain NSP. Media harvested from cells was analysed for release of IL-8 (by ELISA) and cytotoxicity marker adenylate kinase (by Toxilight bioassay). Apoptotic cell death was measured using the Caspase Glo 3/7 assay. In the presence of plantain NSP, TcdA- and TcdB-mediated (A,B) IL-8 release, (C,D) caspase 3/7 activation, and (E,F) cytotoxicity (intracellular adenylate kinase release) were all significantly reduced (N = 2, n = 3; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; Kruskal-Wallis test).