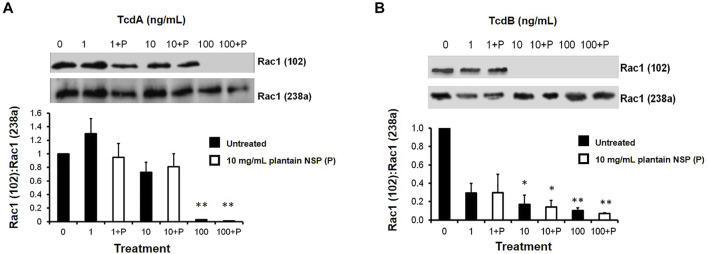
FIGURE 7.
C. difficile toxins A and B mediate increased Rac1 glucosylation within intestinal epithelial cells, which is unaffected by pre-treatment with soluble NSP from plantain. Immunoblot analysis shows an increase in Rac1 glucosylation following treatment with 10 ng/ml (A) toxin A (TcdA) for 24 h and (B) toxin B (TcdB) for 48 h, which is unaffected by pre-treatment of Caco-2 cells with 10 mg/ml soluble plantain NSP (P). Protein bands were analysed by chemiluminescence image densitometry. Mono-glucosylated Rac1 levels (assessed with antibody 102) were normalised to total Rac1 (assessed with antibody 238a), with representative blots shown for N = 3 experiments, n = 3 replicates. Significant differences from non-toxin treated controls, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001; Kruskal-Wallis test.