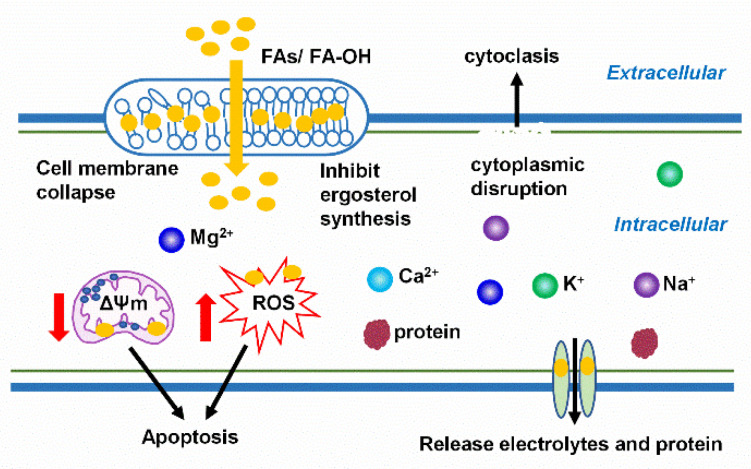
Figure 1.
Antifungal mechanisms of free fatty acids and hydroxy fatty acids. Free fatty acids or hydroxy fatty acids (FAs/FA-OH) insert themselves into the lipid bilayer of the fungal membrane and result in general disruption of the cell membrane, low sterol content, release of intracellular components, cytoplasmic disruption, and ultimately, cell disintegration; they also cause an increase in ROS production and loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential (ΔΨm) and ultimately, apoptosis.