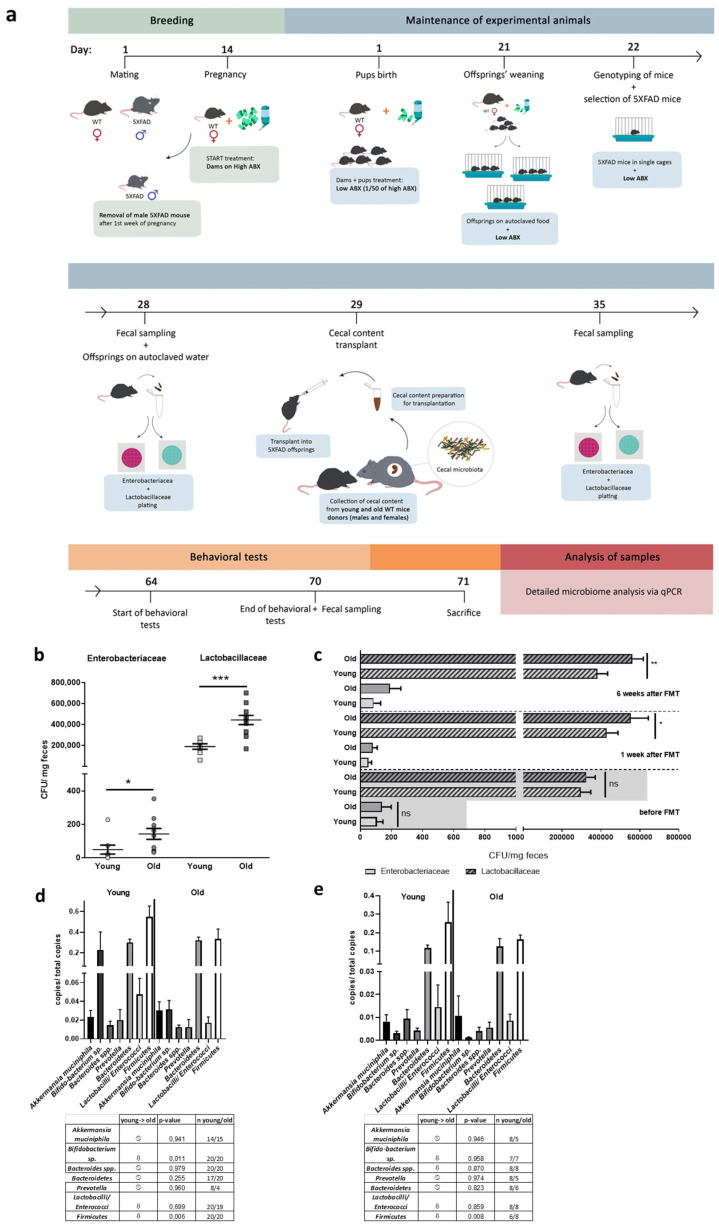
Figure 1.
FMT after pre- and postnatal antibiotics treatment of 5xFAD model mice. (a) Dams were subjected to antibiotics (ABX) treatment via drinking water after two weeks of pregnancy (high ABX). With giving birth, antibiotics dosage was reduced (low ABX) and offspring was kept on this dosage until one day before FMT at the age of about four weeks. Fecal sampling was performed directly before, one week after and six weeks after FMT. (b) Wild type mice aged four weeks (young) or one year (old) were used as donors for FMT. CFUs/mg of feces for Enterobacteriaceae and Lactobacillaceae were assessed by using selective culture plates (n = 8 for young; n = 10 for old). (c) CFUs of animals subjected to FMT were counted on selective culture plates during the experiment (n = 20 per group, 10 female). 5xFAD mice treated with cecal material from young wt mice are designated as “young” while animals treated with material from one year old wt mice are designated as “old”. Samples from transgenic mice without any treatment served as control to monitor the efficacy of the antibiotics’ treatment regime (values given by the height of the grey boxes, see Supplementary Figure S2b). (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001). (d) Besides cultivatable exemplary bacteria, several groups of bacteria were analyzed by qPCR using fecal gDNA from animals six weeks after FMT and specific primer pairs (“young”: 5xFAD treated with cecal material from young wt mice; “old”: 5xFAD treated with cecal material from old wt mice). The table beneath the graph summarizes findings, analyzed independent samples, and p-values (one way Anova with Fisher’s LSD test). (e) For a parallel analysis of the microbiome of untreated young and 1 year old wild type mice, the same analysis as described in (d) was performed on fecal material-derived gDNA of mice without antibiotics-treatment or FMT.