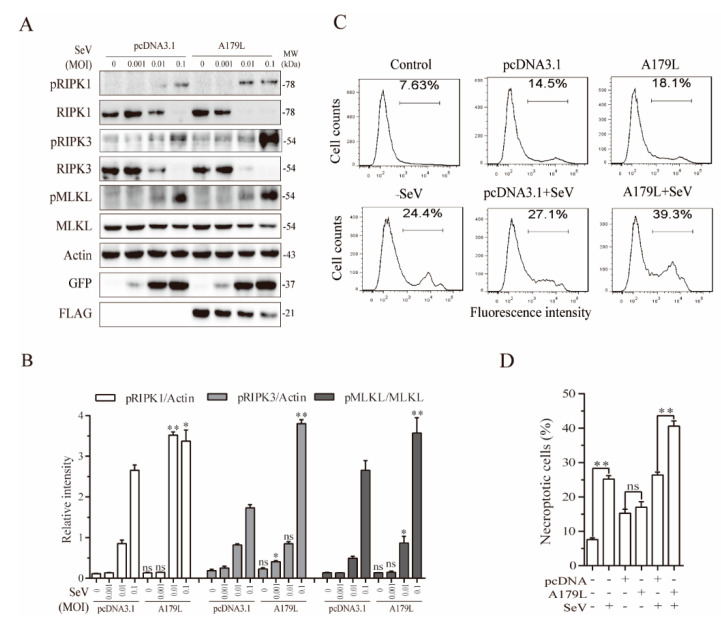
Figure 5.
A179L enhanced Sendai virus-induced necroptosis. (A) IPEC-DQ cells seeded in a 12-well plate were transiently transfected with pcDNA3.1 or the A179L expression vector. After incubation for 24 h, the cells were left uninfected or infected with the indicated dose of Sendai virus and then incubated for 24 h. Cell lysates were prepared and analyzed for the levels of RIPK1S166, RIPK3, MLKL, and their corresponding total proteins. A179L expression was analyzed by Western blot with an anti-FLAG antibody. Sendai virus infection was monitored by Western blot with an anti-EGF antibody. The densities of the bands were analyzed by using NIH Image-J software and normalized by the arbitrary units of their corresponding total protein or β-actin. Data are the mean ± SD of three experiments (B). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, compared to the pcDNA3.1 control; ns, not significant. (C) IPEC-DQ cells seeded in a 6-well plate were left untransfected or transiently transfected with pcDNA3.1or the indicated amount of the A179L expression vector (4 μg each). After incubation for 24 h, the cells were left uninfected or infected with Sendai virus (1 MOI) for 24 h. Single-cell suspensions were stained with Sytox green and analyzed for necroptosis by flow cytometry (C). The results represent the mean percent of cell death ± SD of three independent experiments (D). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.