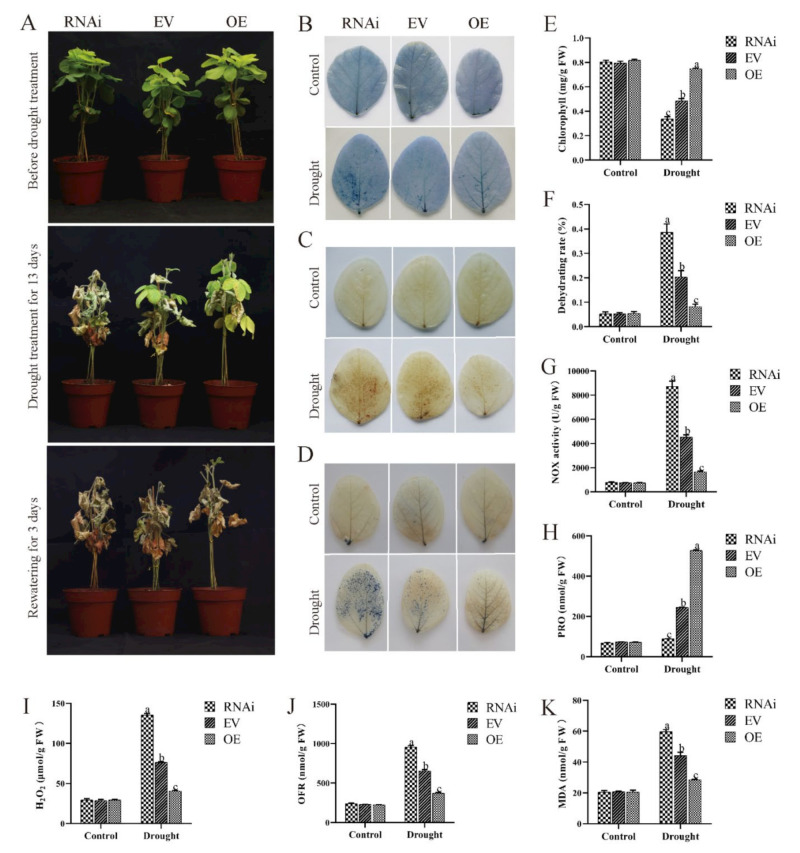
Figure 8.
Under drought treatment, the phenotype of hairy root soybean, the states of difference hairy root plant leaves and the results of physiological index. (A) the seedlings with 2–5 cm hairy roots were grown for five days in pots under non-drought conditions, and then watering was withheld from plants for 13 days. Survival rates of the water-stressed plants were determined three days after rewatering. (B) Trypan blue staining of dead cells (live cells do not stain) of the hairy root soybean plant leaves without irrigation for 11 days. DAB (C) and NBT (D) staining of the hairy root soybean plant leaves of OE, EV and RNAi after drought or non-drought treatment for a week. The depth of color shows the concentrations of H2O2 and O2− in the leaves. Chlorophyll content (E), water-loss rate (F), NOX content (G) proline content (H), H2O2 content (I), O2− content (J), and MDA content (K) were detected in leaves of the hairy root soybean plants OE, EV and RNAi under a week-long drought or non-drought treatment. Three biological replicates were performed, and the values are means ± SD. Values marked with similar letters indicate not statistically significant differences (Student’s t-test: p ≤ 0.05).