Figure 1. Schematic representation of Helicobacter pylori CagA-induced BRCAness.
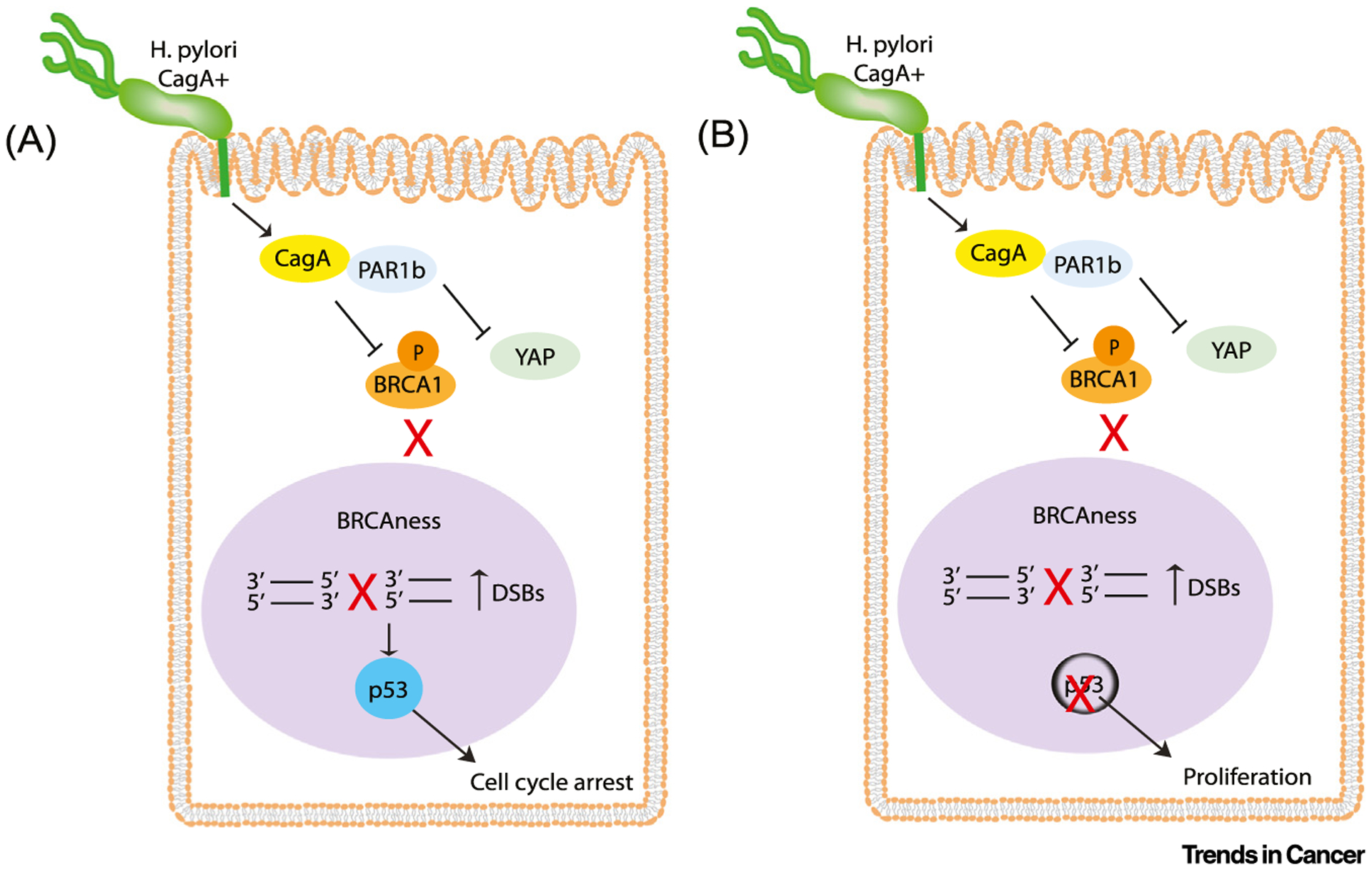
H. pylori translocates CagA into host epithelial cells where it inactivates PAR1b kinase activity, leading to decreased nuclear translocation of BRCA1 and, as a result, increased double strand breaks (DSBs). In parallel, CagA-mediated inhibition of PAR1b activates Hippo signaling and prevents nuclear translocation of Yes-associated protein (YAP), thus inhibiting apoptosis. (A) In the presence of functional p53, p21 is activated and cells enter cell cycle arrest. (B) When cellular p53 is lost or mutated, CagA-expressing cells with BRCAness continue to proliferate.
