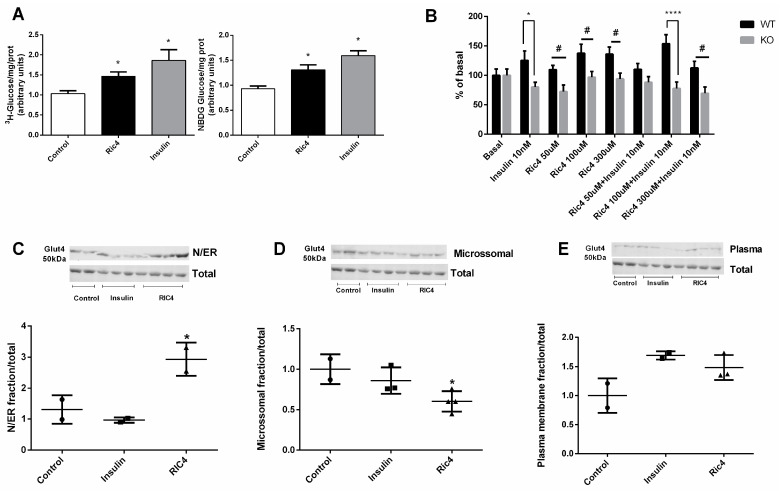
Figure 4.
Glucose uptake and GLUT4 translocation induced by Ric4 in C2C12 cells. C2C12 cells were previously incubated in serum-free and glucose-free DMEM medium, then incubated with HEPES buffer for 30 min and then incubated for a further 30 min in glucose-uptake buffer containing vehicle, Ric4 (100 µM), or insulin (100 nM) in the presence of 3H-glucose (1 µCi/mL) or 2-NBDG (80 µM). After incubations cells were lysed with 50 μL of 0.1 N NaOH and fluorescence or radiation of aliquots from the lysate were measured (A). Epididymal adipose tissue explants (20–25 mg) were incubated in Krebs–Ringer bicarbonate buffer containing glucose 5.5 mM and 1 μCi/mL of 3H-deoxyglucose supplemented with 2% fatty acid-free for 30 min at 37 °C in the presence or absence of insulin (100 nM) or Ric4 (100 µM). The explants were processed to evaluate the uptake of 3H-deoxyglucose (B). Myotubes were previously incubated in serum-free and glucose-free DMEM medium and then treated with control vehicle PBS or Ric4 (100 µM) for 30 min. Proteins from subcellular fractions: N/ER (C), microsomal (D), plasma membrane (E), were isolated and the expression Glut4 was analyzed by Western blot. Images were quantified using ImageJ 1.49 software. The statistical comparisons were performed using analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by ad-hoc Tukey’s test using GraphPad Prism software * p < 0.05; # p < 0.05; **** p < 0.0001.