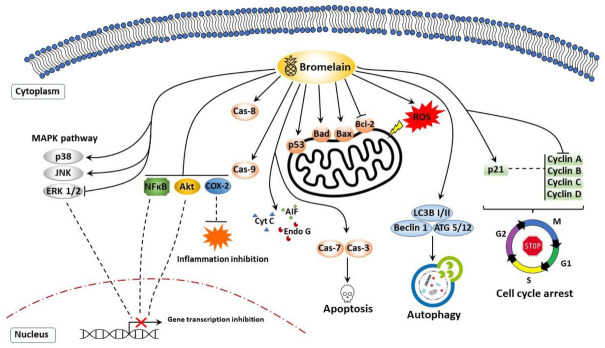
Figure 1.
Possible molecular mechanisms of bromelain’s anti-tumor activity are realized at 3 levels of cellular metabolism. In vitro and in vivo studies have shown that bromelain inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells primarily by I) modulating the expression of genes crucial for cell differentiation and proliferation (MAPK signaling pathway, Akt, Cox-2, NF-κB), II) induction of cell death by apoptosis/autophagy, and III) blocking the cell cycle by inhibiting cyclins which are necessary for this process.