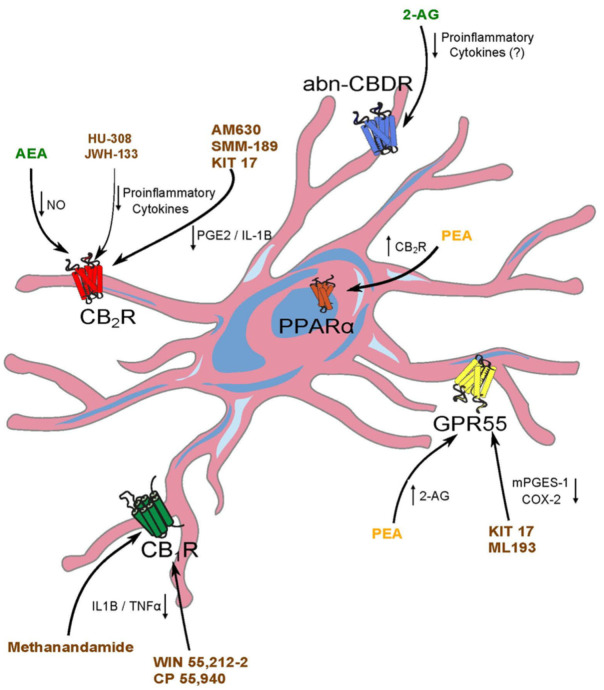
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the interactions of (endo)cannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoid compounds with microglia in the context of epilepsy and neuroinflammation. Endocannabinoids (green) interact with CB2 receptors and other non-classical receptors (GPR55, PPAR and abn-CBDR). Fatty acid amides, such as PEA, interact with non-classical receptors (yellow), while synthetic cannabinoid effects (brown) involve mainly CB1 and CB2 receptors.