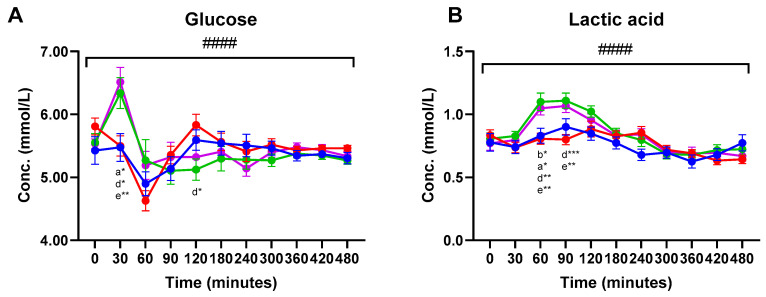
Figure 2.
Postprandial plasma concentrations (mean ± SEM) of (A) glucose and (B) lactic acid. ● MCI Drink, ● MCI Gel, ● Hom. Cheese, ● Cheese. # indicate significant meal-time interactions: #### (q <0.0001). Letters indicate significant differences in post-hoc tests: a MCI gel vs. Cheese, b MCI gel vs. Hom. Cheese, c MCI gel vs. MCI drink, d MCI drink vs. Hom. Cheese, e MCI drink vs. Cheese, f Hom. Cheese vs. Cheese. Asterisks indicate level of significance: * (p <0.05), ** (p <0.005), *** (p <0.0005)). For 3-hydroxybutyric acid, a significantly higher plasma concentration was found at 360 min following consumption of the MCI Gel compared to the MCI Drink (Table 1). For acetoacetic acid, significant differences were found at 360 min. Thus, significantly higher plasma concentrations of acetoacetic acid were found after consumption of MCI Gel compared to the MCI Drink and Hom. Cheese, and a significantly higher concentration was found after Cheese consumption compared to the MCI Drink. For pyruvic acid, significant differences were found after 60 and 90 min. At 60 min, Cheese consumption resulted in significantly higher plasma pyruvic acid concentrations compared to MCI Gel and near-significant differences were higher compared to the MCI Drink (p = 0.069). After 90 min, significantly higher concentrations were found after consumption of Cheese and Hom. Cheese compared to the MCI Drink.