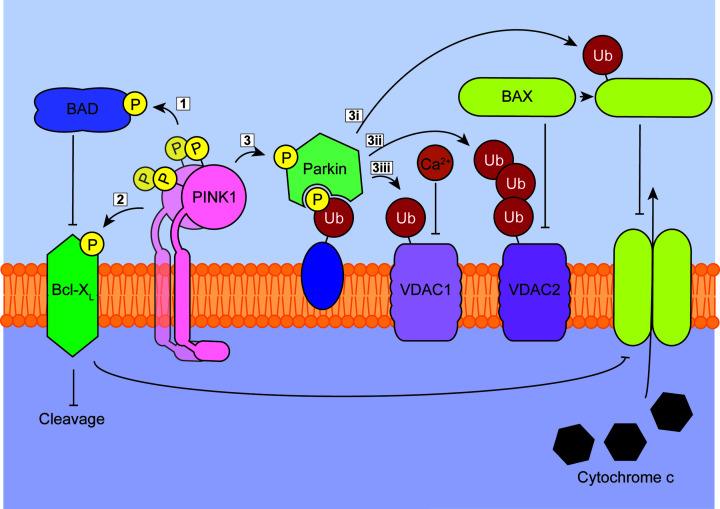
Figure 3. Anti-apoptotic roles of PINK1.
PINK1 phosphorylation acts as an anti-apoptotic signal through several substrates. (1) Phosphorylated BAD is inhibited in its normal pro-apoptotic binding to Bcl-XL on the OMM. (2) Direct phosphorylation of Bcl-XL functions to prevent its cleavage, thus encouraging its inhibition of the formation of BAX pores and the subsequent release of cytochrome c. (3) Parkin phosphorylation also provides several anti-apoptotic influences, including: (3i) the ubiquitination of VDAC1, regulating Ca2+ influx; (3ii) the polyubiquitination of VDAC2, inhibiting the association of BAX and (3iii) the direct ubiquitination of BAX, inhibiting the formation of pores on the OMM.