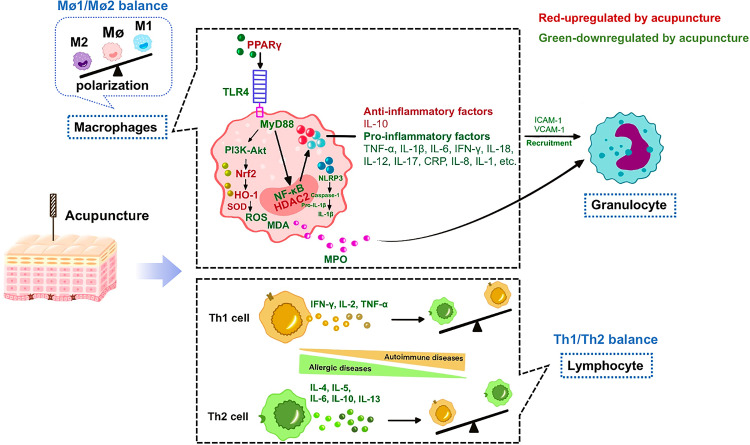
Figure 2.
Common anti-inflammatory effects of acupuncture in various systems. Factors in red are up-regulated by acupuncture, while factors in green are down-regulated by acupuncture. Acupuncture fights against inflammation using two major pathways: regulating macrophage polarization and preserving Th cell balance.
Abbreviations: PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; TLR4, Toll-like receptors; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; SOD, superoxide dismutase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; MDA, malondialdehyde; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; Nrf2, NFE-related factor 2; MPO, myeloperoxidase; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor protein 3; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; INF-γ, interferon γ; p38 MAPK, p38 mitogen activated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; HDAC2, histone deacetylase inhibitor 2; CRP, C-reactive protein; ICAM-1, intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1.