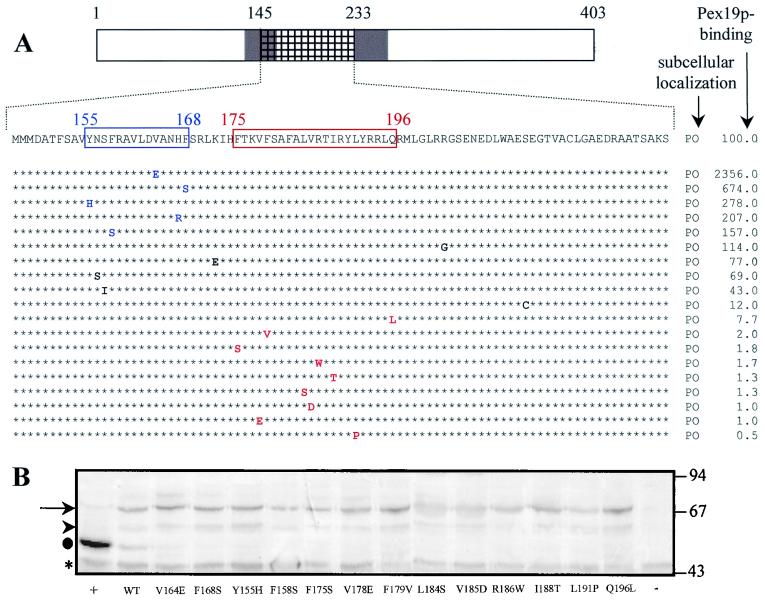
FIG. 6.
The Pex13p amino acids from position 175 to 196 are essential for Pex19p binding but not for protein sorting. (A) The missense mutations obtained by random mutagenesis were separately introduced into the full-length BD-Pex13p and Pex13p-GFP molecules. The corresponding mutants were analyzed for their ability (i) to target the GFP reporter protein to the peroxisomes (PO) and (ii) to bind Pex19p in the two-hybrid system. To compare the binding affinities between the different mutants, the expression of the yeast two-hybrid lacZ reporter gene was quantitatively measured by using o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside as the substrate. The results (average of three independent clones), expressed as the percentage of the observed β-galactosidase activity of wild-type BD-Pex13p, are shown. Amino acids that, when mutated, enhance Pex19p binding are blue. Mutations resulting in a negative staining pattern when assayed for β-galactosidase activity using a filter assay with X-Gal as the substrate are red. TMDs are shaded, and the fragment that originally was subjected to error-prone PCR is hatched. (B) The mutants displaying an enhanced or reduced Pex19p-binding affinity were equally expressed in the yeast reporter strain SFY526. Double yeast transformants were selected and analyzed for the expression of the BD-fusion proteins by using an anti-Pex13p antiserum. →, full-length BD-Pex13p proteins; ▸, putative degradation products; ●, the C-terminal 269 amino acids of Pex13p, expressed as a BD-fusion protein (+); *, nonspecific anti-Pex13p-cross-reactive yeast proteins. In the yeast transformant (−), the BD-domain was fused to Pex14p. The migrations of the molecular mass markers (masses in kilodaltons) are indicated.