Figure 3: Antitumor mechanisms of VBP.
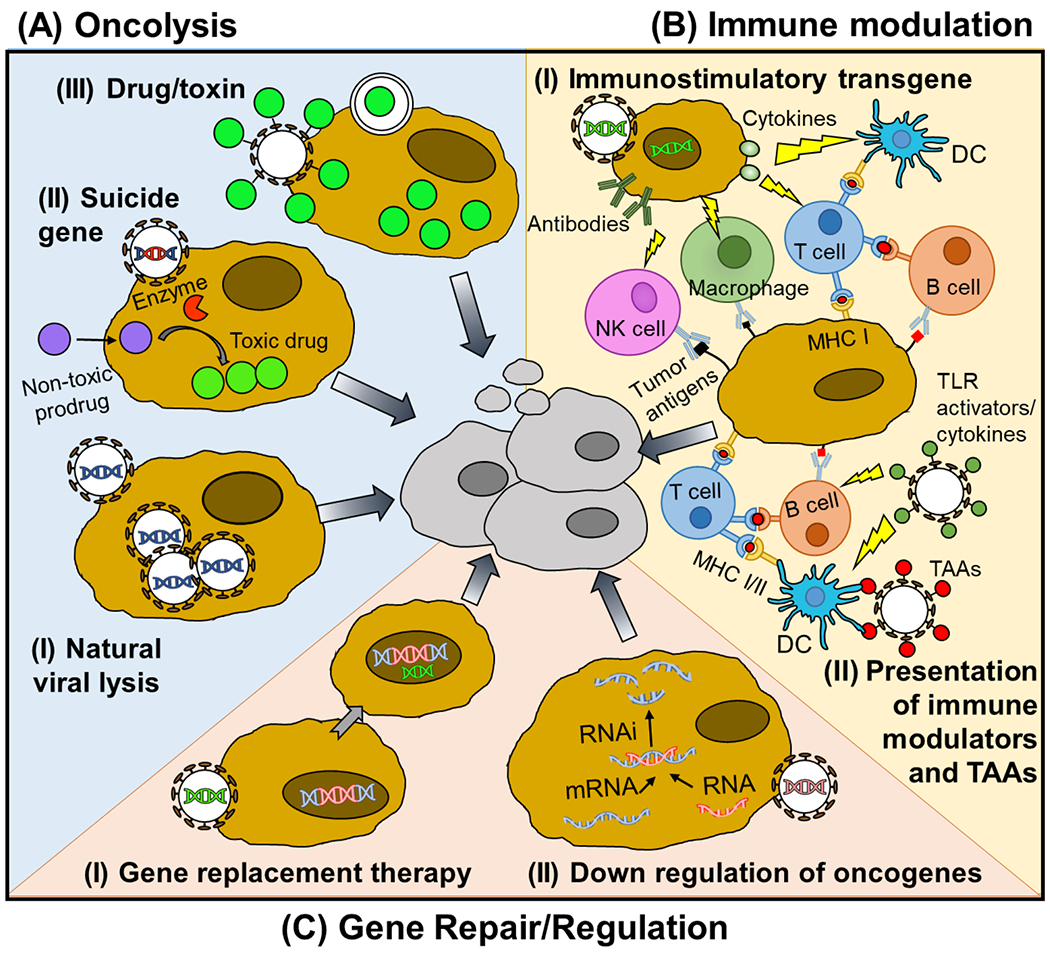
Antitumor mechanism of VBP can be divided into three groups. (A) VBPs can promote oncolysis through (I) natural viral lytic mechanisms, (II) delivery of a suicide gene, or (III) delivery of a drug or toxin. (B) VBPs can also relieve the immunosuppressive environment of the TME and promote a tumor-specific adaptive immune response through either (I) delivery of immune stimulating transgenes to tumor cells, encoding for example cytokines or antibodies, or (II) delivery of cancer antigens and immunostimulatory molecules to APCs. (C) Finally, VBPs can restore cellular antitumor functions through delivery of (I) tumor suppressive transgenes or (II) interfering RNA that degrades oncogenic miRNA or mRNA.
