Figure 1. Evolutionary conservation of human sodium channel genes.
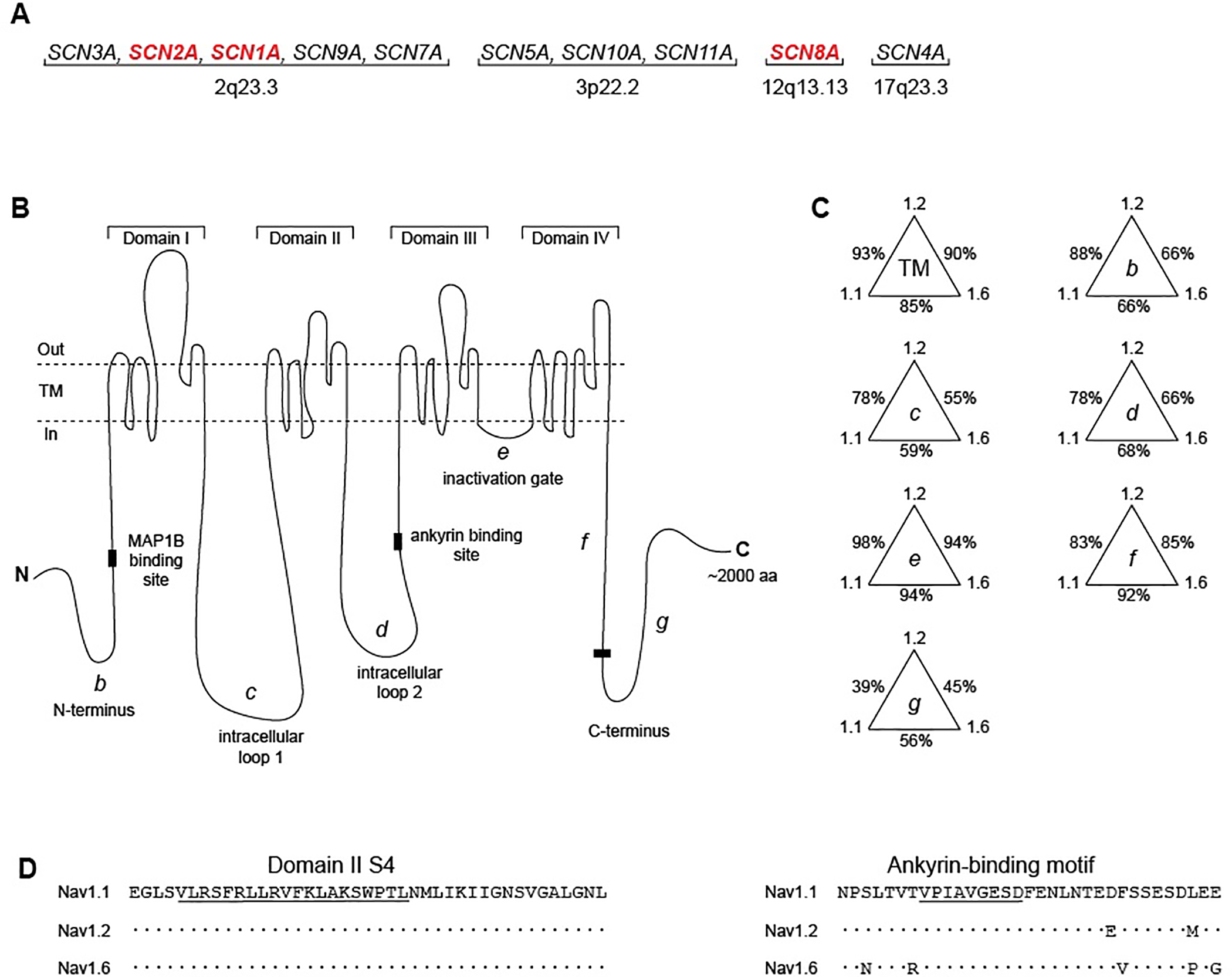
(A) Chromosomal locations of human voltage-gated sodium channel genes. The channels with high expression in the adult CNS (red) are covered in this review. (B) The voltage-gated sodium channel α subunit is composed of four transmembrane domains separated by intracellular loops. TM, transmembrane segments; b, N-terminus; c, cytoplasmic loop 1; d, cytoplasmic loop 2; e, inactivation gate; f, proximal half of C-terminus; g, distal half of C-terminus. (C) Percent conservation of amino acid sequence in the protein domains of SCN1A (Nav1.1), SCN2A (Nav1.2), and SCN8A (Nav1.6). Labels refer to domains in panel B. (D). Examples of regions of high sequence conservation in transmembrane segment DIS4 (left) and around the 9 residue ankyrin binding motif (right) 38. Dots represent amino acid identity.
