Figure 4. HPV16 full length transcript structure in primary HPVOPC tumors.
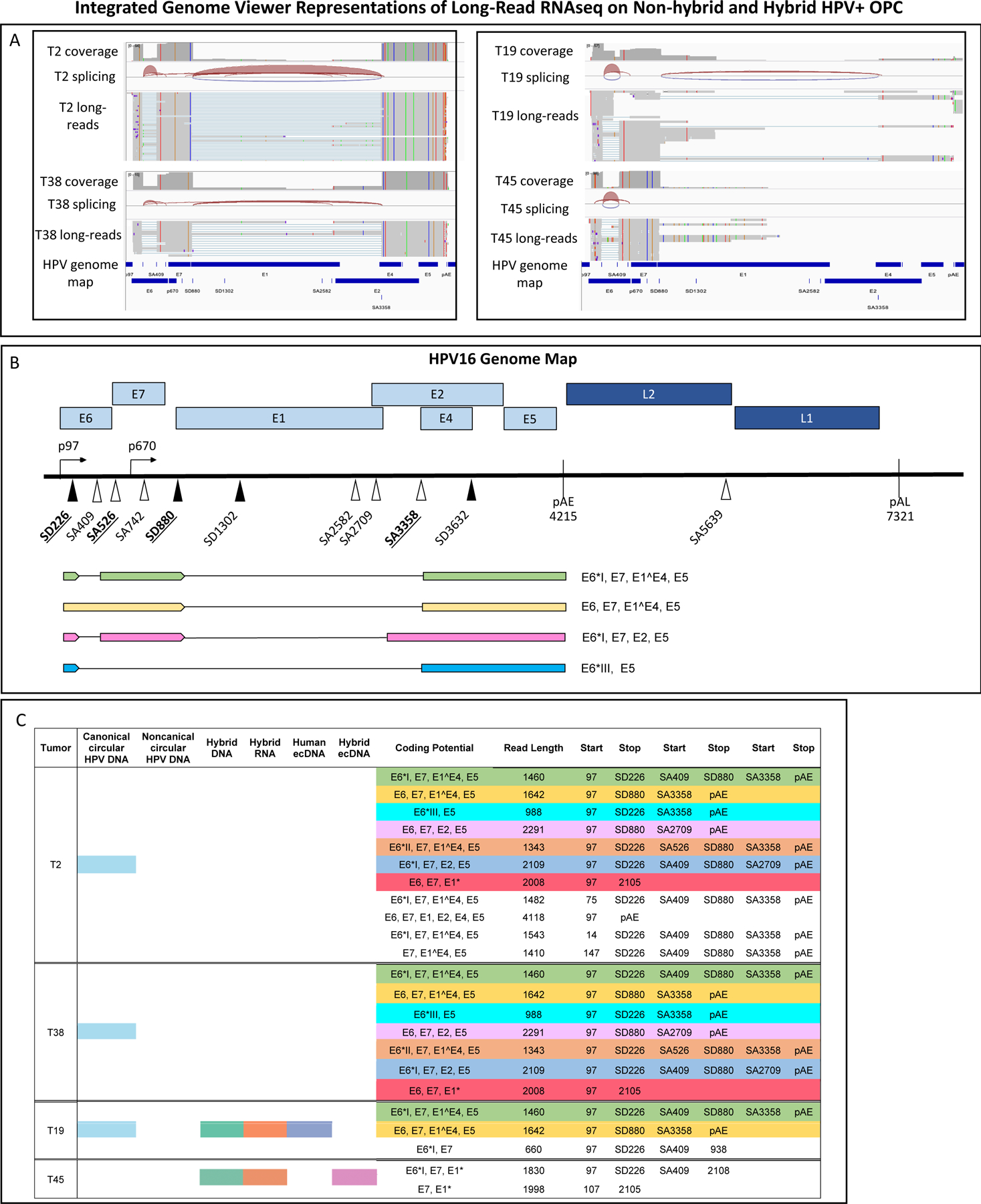
A) Integrated Genome Viewer graphics are displayed of long-read RNA whole genome poly A transcript sequencing on a subset of two tumors without hybrid transcripts (T2 and T38), one human ecDNA tumor with hybrid transcript expression (T19), and one hybrid ecDNA tumor with hybrid transcripts (T45).
B) The most common long read Iso-Seq transcripts mapping to HPV exclusively are depicted with their coding potential. The single most common full-length transcript in non-hybrid tumors was 1,476 nt long, beginning at the p97 promoter with splicing at SD226-SA409 and SD880-SA3358 extending to the early polyA tail, with coding potential for the E6 oncoprotein variant E6*I defined by SD226-SA409, full-length E7, full-length E4, and full-length E5.
C) Poly-A tail-based long-read RNA sequencing of non-integrated and integrated tumors with mapping of full-length transcripts to HPV-16 genome demonstrates the transcriptome patterns in primary tumors. Identical isoforms have been color-coded. Read counts fewer than 5 were discarded. Full length coverage counts per Iso-Seq protocol are not proportionate to transcript quantity. Tumors without hybrid transcripts (T2 and T38) have distinct transcriptomes from those with hybrid transcripts and with ecDNA (T19, T45).
