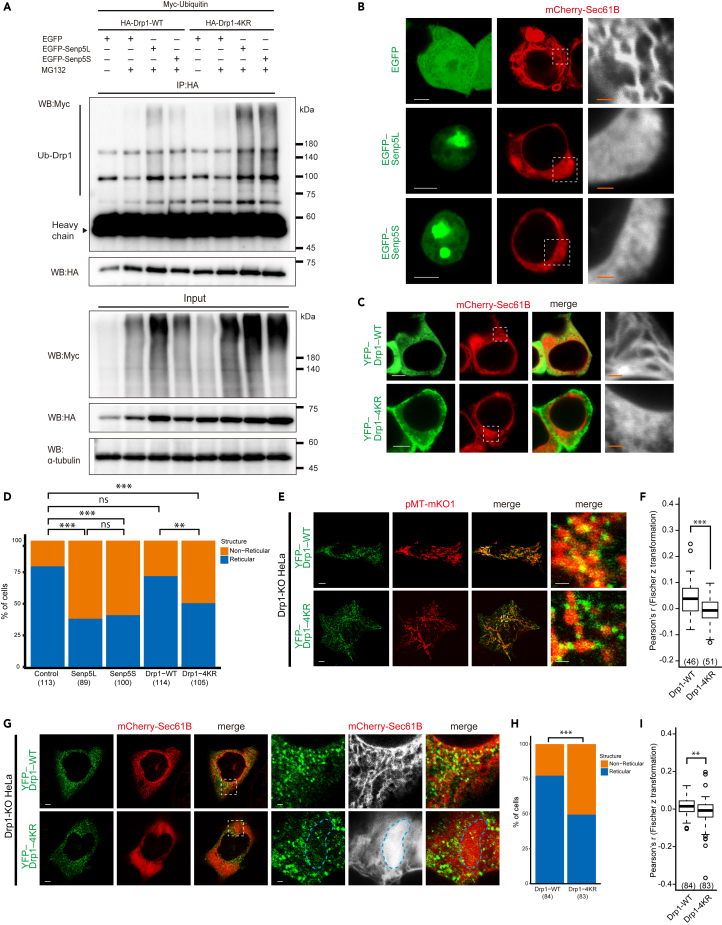
Figure 4.
Senp5L/5S are involved in Drp1 ubiquitination and ER dynamics
(A) SUMOylation prevents the ubiquitination of Drp1. HEK293T cells were transfected with Myc-Ubiquitin and HA-Drp1-WT or HA-Drp1-4KR constructs with or without pretreatment with 5 μM MG132 for 3 h. To evaluate the effect of Senp5 on ubiquitination of Drp1, cells were additionally co-transfected with EGFP-Senp5L, EGFP-Senp5S, or (as a control) EGFP. Subsequently, each cell lysate was immunoprecipitated with anti-HA and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-Myc, anti-HA, or anti-α-tubulin. Panels show representative immunoblots for the input lysate (bottom panels) and IP samples (top panels). Drp1 conjugated with Myc-ubiquitin is observed as ladder or smear bands with higher molecular weight (vertical line). Heavy chain, immunoglobulin heavy chain of the HA antibody.
(B) Senp5L and 5S induce morphological change in the ER. 293T cells were transfected with EGFP, EGFP-Senp5L, or EGFP-Senp5S (green), together with mCherry-Sec61B (red) to monitor the ER network. Right column: higher magnification of the square areas showing mCherry-Sec61B+ ER morphology (gray scale).
(C) SUMOylation at the D-octadecapeptide of Drp1 is required for inducing tubulation of the ER. HEK293T cells were transfected with mCherry-Sec61B (red) and YFP-Drp1-WT or YFP-Drp1-4KR (green). Right column: higher magnification of the square areas (gray scale).
(D) Quantified comparison of the effect of Senp5L, Senp5S, or Drp1-4KR overexpression on ER morphology. The stacked bar chart shows the percentages of cells that exhibit a tubulated reticular ER or a sheet-like, non-reticular ER. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of cells observed in two independent experiments in (B) and (C). ns, not significant; ∗∗, p < 0.01; ∗∗∗, p < 0.001; chi-square tests with Holm-Bonferroni correction.
(E) Drp1 SUMOylation alters co-localization with mitochondria. Drp1-KO HeLa cells were transfected with pMT-mKO1 (red) and YFP-Drp1-WT or YFP-Drp1-4KR (green). Right column, higher magnification of the boxed areas.
(F) Quantified comparison of the co-localization of YFP-Drp1-WT or YFP-Drp1-4KR with mitochondria. Fischer z-transformation of Pearson's correlation coefficient was used as a co-localization index and summarized in box and whisker plots. ∗∗∗, p < 0.001; Welch's t test.
(G) Drp1 SUMOylation alters co-localization with ER. Drp1-KO HeLa cells were transfected with mCherry-Sec61B (red) and YFP-Drp1-WT or YFP-Drp1-4KR (green). Right columns, higher magnification of the boxed areas. Hatched region in panels denote the non-reticular ER.
(H) Quantification of the effect of YFP- Drp1-WT or Drp1-4KR overexpression in Drp1-KO HeLa cells on ER structure. The stacked bar chart shows the percentages of cells that exhibit a tubulated reticular ER or a sheet-like, non-reticular ER. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of cells observed in three independent experiments. ∗∗∗, p < 0.001; chi-square test.
(I) Quantified comparison of the co-localization YFP-Drp1-WT or YFP-Drp1-4KR with ER. Fischer z-transformation of Pearson's correlation coefficient was used as a co-localization index and summarized in box and whisker plots. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of cells observed in three independent experiments. ∗∗, p < 0.01; Welch's t tests. Scale bars, 5 μm in (B), (C), (E), and (G) and 1 μm in the magnified view.