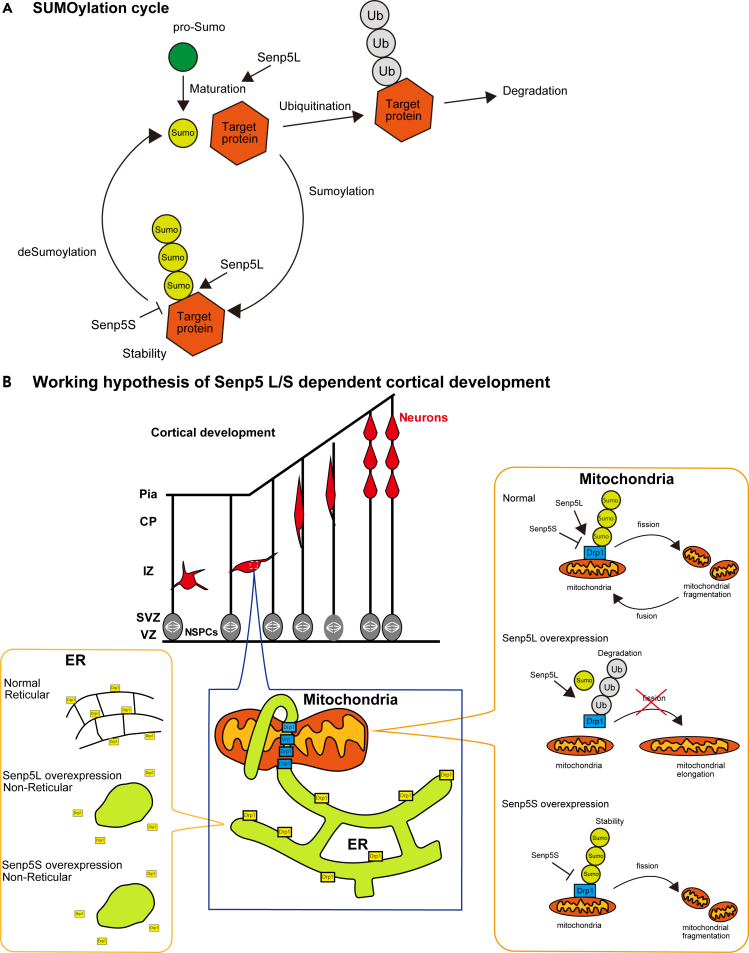
Figure 7.
Schematic model of how Senp5L and Senp5S mediate Drp1 SUMOylation
(A) Shown is the SUMOylation cycle and the roles of Senp5L/5S. Senp5L removes SUMO from the target proteins (deSUMOylation) and Senp5S promotes SUMOylation, probably by substrate competition with other Senps, including Senp5L. Senp5L also is known to cleave pro-SUMO to produce the mature and conjugatable form of SUMO.
(B) Hypothetical function of Senp5L/S in regulating cortical development. A tuned balance between Senp5L and Senp5S expression is indispensable for neuronal polarization and cortical organization. Overexpression of Senp5L accelerates deSUMOylation and ubiquitination of Drp1, and thus mitochondrial fusion. Senp5L overexpression also induces the morphological transformation of ER into the non-reticular form, which reduces the availability of interface sites between the peripheral ER and mitochondria, further promoting mitochondrial elongation. However, overexpression of Senp5S enhances Drp1-SUMOylation, resulting in the stabilization of Drp1 and mitochondrial fragmentation. Enhanced SUMOylation due to Senp5S upregulation may lead to disruption of the interaction between the ER and mitochondria and a subsequent collapse of the reticular ER.