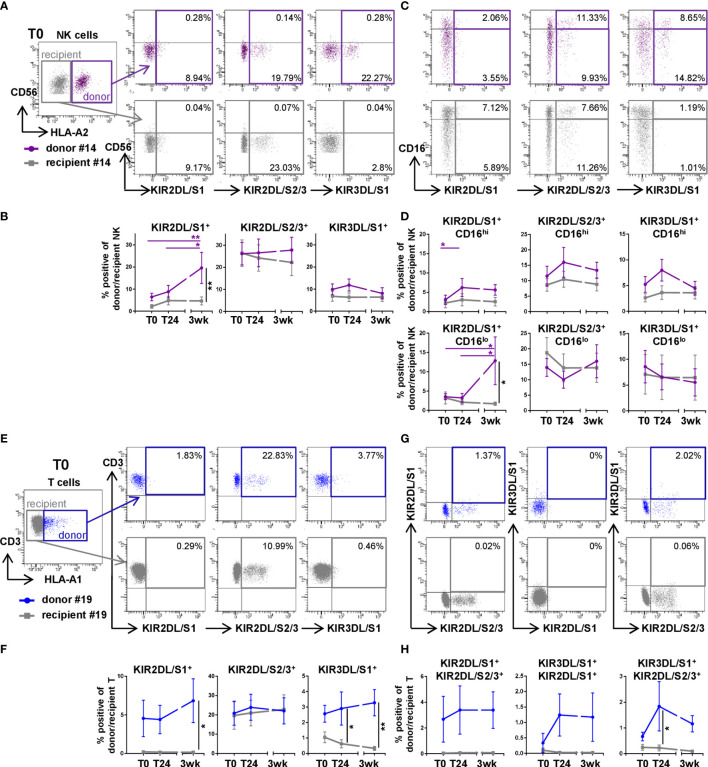
Figure 2.
The proportion of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR) on donor NK and T cells is higher compared to recipient cells within the first three weeks after DLTx. (A–D) KIR2DL/S1, KIR2DL/S2/3 and KIR3DL/S1 surface expression on NK cells (n=14) was analyzed in peripheral blood of double-lung transplant recipients directly post (T0), 24 hours (T24) and three weeks after transplantation (3wk). Donor and recipient cells were distinguished by HLA mismatch: NK cells of the representative donor #14 were identified by HLA-A2 staining (A, C) T cells of the representative donor #19 were identified by HLA-A1 staining (E, G), the gating strategies are shown in Figures 1C and Supplementary Figure 1 . (A) Representative FACS plots (T0) and (B) frequencies of donor (purple colored squares) and recipient (grey colored squares) KIR on NK cells. (C) Representative FACS plots (T0) and (D) frequencies showing KIR expression on CD16hi and CD16lo NK cells. (E–H) The same KIR repertoire was assessed for T cells (n = 14) in peripheral blood of DLTx patients for the indicated time points. T cells of donor #19 were stained using anti-HLA-A1-specific Ab. (E) Representative FACS plots and (F) frequencies of KIR on donor (blue colored squares) and recipient (grey colored squares) T cells are displayed. (G) Representative FACS plots and (H) frequencies describing double positive KIR surface expression on T cells. Statistical analysis: two-way ANOVA with Sidak´s multiple comparison test and Tukey´s multiple comparison test. Data are shown as mean ± SEM, asterisks indicate p-values with *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.