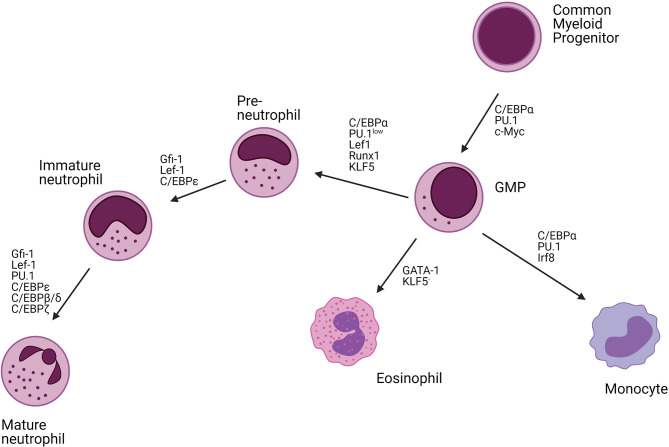
Figure 3.
Transcription factors regulating neutrophil differentiation. Neutrophils mature from hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) in the bone marrow (BM). These HSCs are self-reviewal and can differentiate into all immune cells. The common myeloid progenitor (CMP) cells give rise to the myeloid lineage including neutrophils, monocytes, and eosinophils. C/EBPα is the main transcription factor driving myeloid differentiation. Together with PU.1, and c-Myc, C/EBPα drives granulocyte-monocyte progenitor cell (GMP) differentiation. High levels of C/EBPα, PU.1, and Irf8 further drive monocyte development, high levels of GATA-1 eosinophil development, whereas C/EBPα, Lef1, Runx1, KLF5 together with low expression of PU.1 enhance neutrophils development. Neutrophil maturation is further driven by Gfi-1, Lef-1, C/EBP transcription factors (C/EBPϵ, C/EBPβ, C/EBPδ, C/EBPζ), and PU.1. C/EBP, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein; Irf8, Interferon regulatory factor 8; Lef1, Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1; Runx1, Runt-related transcription factor 1; KLF5, Krüppel Like Factor 5; GFI1, Growth Factor Independent 1 Transcriptional Repressor.