FIGURE 1.
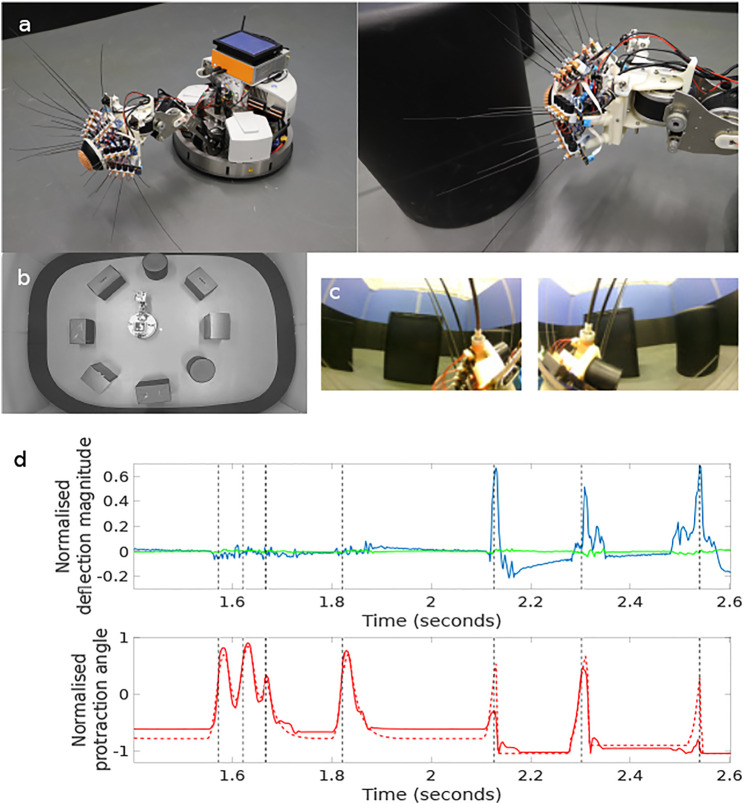
The WhiskEye robot (A) has 24 actuated tactile whiskers and camera eyes on its head mounted at the end a 3 dof neck and omnidrive Robotino body. Simultaneous visual frames [panel (C), left and right eye cameras] and tactile samples are taken at the point of peak whisker protraction as indicated by the black vertical dashed lines in the plots of panel (D). The example time series data shown in panel d are taken from a single whisker through 7 whisk cycles with only the final 3 whisks making contact with an object. The red dashed trace in the lower plot is the drive or desired protraction angle of the whisker scaled to ±1 of the full whisk angle range of ±80 degrees of rotation. The solid red line is the measured protraction angle of the whisker (θ whisk ) which can be inhibited by contacts as is clear on the fifth whisk. The blue trace in the upper plot is the x- and the green the y-deflection of the whisker scaled to ±1 of maximum deflection magnitude. The three positive whisker contacts are clear in the final three whisks of this sample. The x, y, and θ whisk samples taken at the point of peak protraction for all 24 whiskers constitute the tactile “view” of the robot at that instance. The experimental arena shown in panel (B), was populated with matt black cylinders and boxes, the configuration was changed between collecting data to train the networks and for testing.