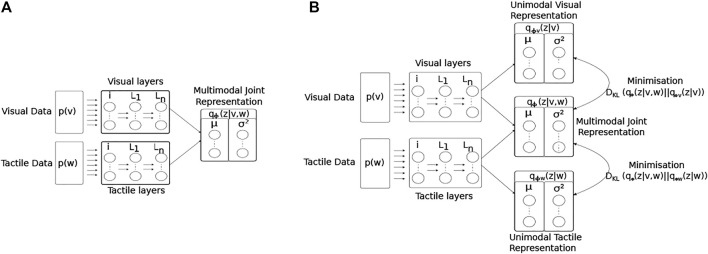
FIGURE 14.
Architectural diagrams of the encoder networks of the two JMVAE models; (A) JMVAE-zero, and (B) JMAVAE-kl. Both networks attempt to represent the two input modalities (visual p(v) and tactile p(w)) as a joint multimodal latent representation q ϕ (z|v, w). This is done by minimising both the reconstruction error for each modality, and the KL-divergence (D KL ) between a standard normal distribution and the joint multimodal distribution. The resulting continuous distribution is encoded by the activity of two parallel layers of nodes representing the mean and variance (μ, σ 2) of each latent dimension. The JMVAE-kl model trains 2 further encoders, one using only visual input q ϕv (z|v) and the other only tactile q ϕw (z|w), such that the KL-divergence measures between the unimodal and multimodal approximate distributions can be included into the loss function during training.