FIG. 5.
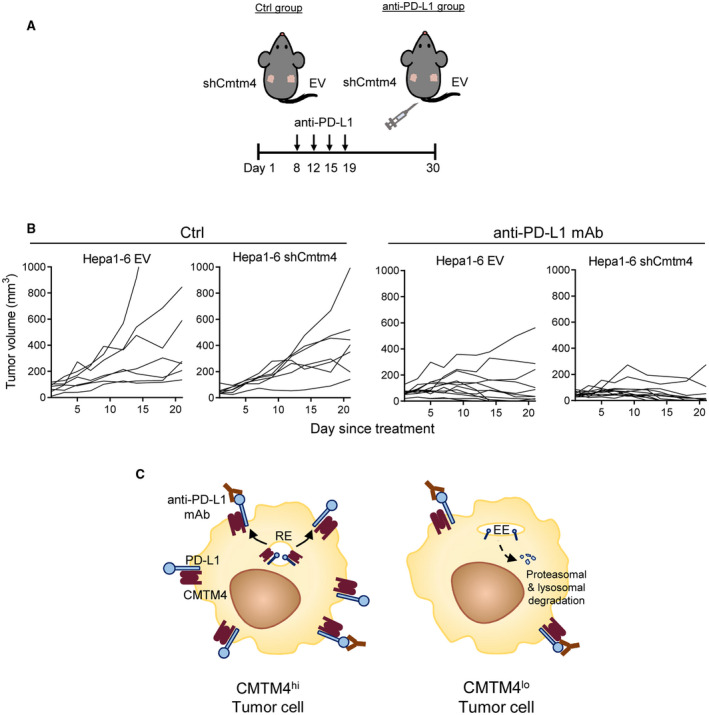
Inhibition of CMTM4 sensitized HCC toward PD‐L1 blockade in mouse. (A) Scheme of experimental design. A total of 3 × 106 of Hepa1‐6 EV and Cmtm4‐knockdown (shCmtm4‐1) cells were subcutaneously implanted into the right and left sides of the lateral flank of wild‐type mice, respectively. Four doses of anti‐PD‐L1 mAb or saline control were administered by intraperitoneal injection during weeks 2‐3 (10 mg/kg/dose). Control group, n = 7; anti‐PD‐L1, group n = 12. (B) Growth curves of individual tumors, measured from the commencement of anti‐PD‐L1 treatment onward. (C) Schematic diagram explaining the therapeutic effect of CMTM4 inhibition in anti‐PD‐L1 immunotherapy. In CMTM4hi tumor cells, anti‐PD‐L1 monoclonal antibodies fail to occupy all PD‐L1 binding sites (left), whereas with lowered PD‐L1 surface expression in CMTM4lo tumor cells, anti‐PD‐L1 mAb is able to completely abrogate PD‐1/PD‐L1 signaling between T cells and tumor cells and hence fully unleash T cell–mediated antitumor immunity (right). Abbreviations: Ctrl, saline control; EE, early endosome; RE, recycling endosome.
