FIG. 4.
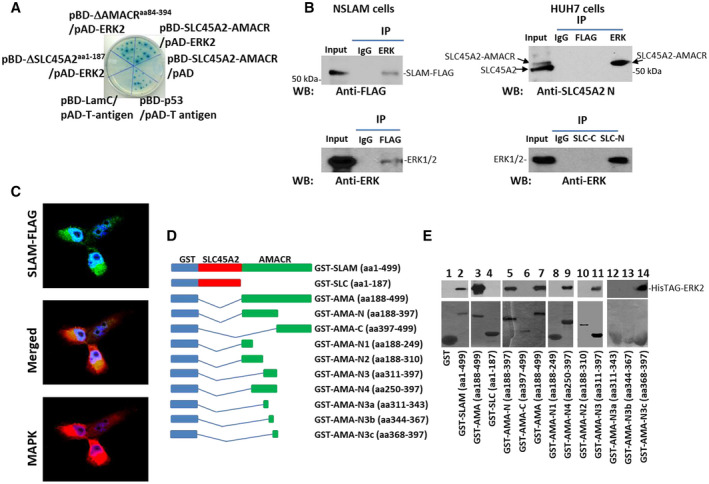
SLC45A2‐AMACR interaction with ERK. (A) Yeast two‐hybrid validation of the interaction between SLC45A2‐AMACR and ERK. Cotransfection of pBD‐SLC45A2‐AMACR and pAD‐ERK2 resulted in colonies grown in SD‐Ade/‐His/‐Leu/Trp agar plates and positive for α‐galactosidase. The interaction between BD‐p53 and activation domain (AD)‐T‐antigen was used as the positive control, while the interaction between BD‐Lamin C (LamC) and AD‐T‐antigen was used as the negative control. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of SLC45A2‐AMACR and ERK in cell cultures. Left panel: Coimmunoprecipitation in NSLAM cells induced to express SLC45A2‐AMACR‐FLAG (SLAM‐FLAG). Top left: Immunoblotting using an antibody specific for FLAG on the immunoprecipitate of ERK antibody or control mouse IgG. Bottom left: Immunoblotting using antibody specific for anti‐ERK on the immunoprecipitate of FLAG antibody or control mouse IgG. Right panel: Coimmunoprecipitation in HUH7 cells. Top right: Immunoblotting using an antibody specific for the N‐terminus of SLC45A2 on the immunoprecipitate of ERK antibody or control mouse IgG or FLAG antibody. Bottom right: Immunoblotting using antibody specific for ERK on the immunoprecipitate by the antibody specific for the N‐terminus of SLC45A2 or control mouse IgG or SLC45A2 C‐terminus antibody. (C) Colocalization between SLC45A2‐AMACR‐FLAG and ERK using antibodies specific for ERK and FLAG (20x images). (D) Schematic diagrams of deletion constructs of GST‐SLC45A2‐AMACR. The GST, SLC45A2, and AMACR domains are indicated. (E) Binding assays between GST‐SLC45A2‐AMACR mutants and recombinant HisTAG‐ERK2. Top: Immunoblotting of HisTAG‐ERK2 to detect the binding between HisTAG‐ERK2 and SLC45A2‐AMACR mutants using an antibody specific for ERK. Bottom: Coomassie blue staining of GST‐SLC45A2‐AMACR mutants. Abbreviations: AD‐T, AMA, AMACR; IP, immunoprecipitation; LamC, SD‐Ade/‐His/‐Leu/Trp, synthetic‐defined adenine, histidine, leucine and tryptophan; SLC, SLC45A2; SLC‐C, SLC45A2 C‐terminus; SLC‐N, N‐terminus of SLC45A2; WB, western blot.
