Figure 1.
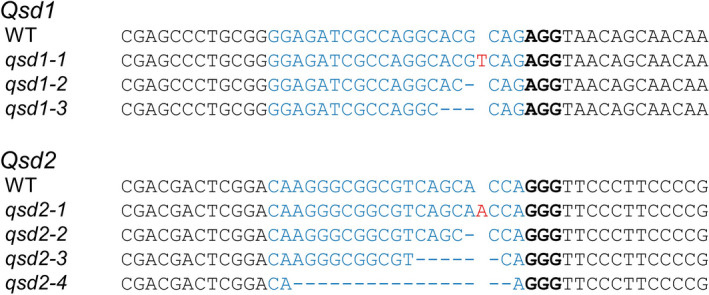
Comparison of DNA sequences for the Cas9/gRNA target sites in Qsd1 and Qsd2 in the wild type and mutants. Sanger sequencing was performed to detect mutations in Qsd1 and Qsd2. Wild‐type, WT; qsd1 mutants, qsd1‐1 to qsd1‐3; qsd2 mutants, qsd2‐1 to qsd2‐4. qsd1‐1, 1‐bp insertion; qsd1‐2, 1‐bp deletion; qsd1‐3, 3‐bp deletion; qsd2‐1, 1‐bp insertion; qsd2‐2, 1‐bp deletion; qsd2‐3, 6‐bp deletion; qsd2‐4, 17‐bp deletion. These representative mutants were used for further analysis; other mutants are listed in Figure S1. The sequence targeted by the gRNA (protospacer) is shown in blue, the protospacer‐adjacent motif (PAM, bound by the Cas9 enzyme) is in bold, dashes indicate deletions, and red nucleotides indicate insertions.
