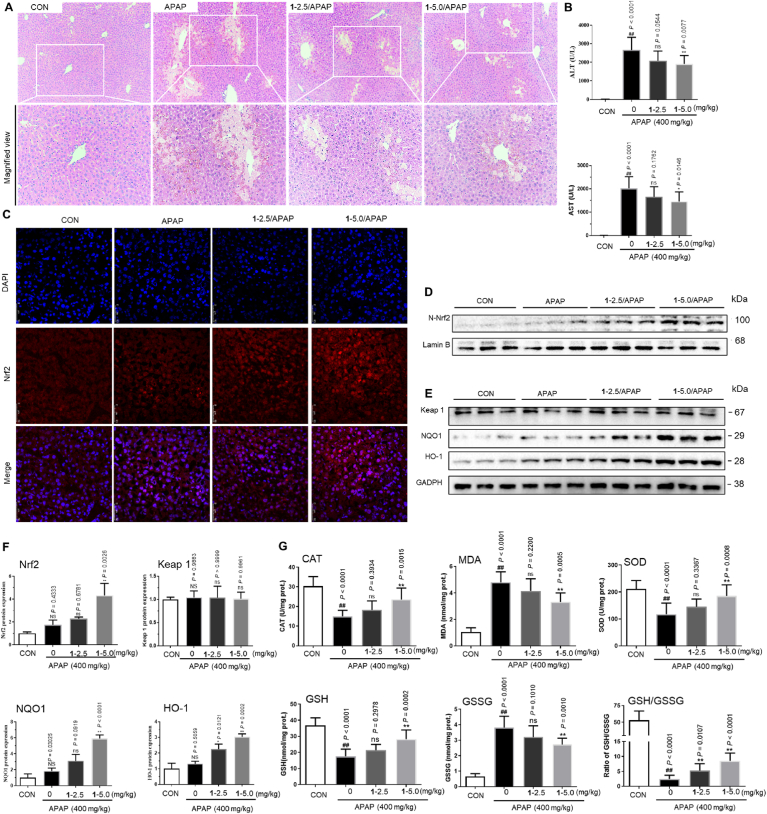
Fig. 5.
Complex 1 alleviates APAP-induced acute liver injury in mice. (A) Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of liver tissue sections. (B) Serum levels of alanine aspartate transaminase (AST) and aminotransferase (ALT). 1 induces nuclear translocation of Nrf2. Immunofluorescence staining of Nrf2 (C) and Western blot analysis of Nrf2 in the nucleus (D). (E) Effect of 1 and ML334 on the HO-1 and NQO1 levels by Western Blotting. (F) 1 reduced APAP-induced liver injury was involved in the upregulation of Nrf2-mediated antioxidative protein. Immunoblots analysis of nuclear Nrf2 (A) and Keap1 (B) expressions respectively, and Nrf2 downstream target proteins NQO1 (C) and HO-1 (D). Lamin B was used as the loading control. (G) Complex 1 alleviated APAP-induced hepatic oxidative stress. Hepatic levels of MDA, GSH, GSSG, GSH/GSSG, and enzyme activities of CAT and SOD were determined after the APAP challenge for 6 h. P values were calculated using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison test. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3 mice). ##P < 0.01 vs. Control (CON) group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. APAP-induced model group.