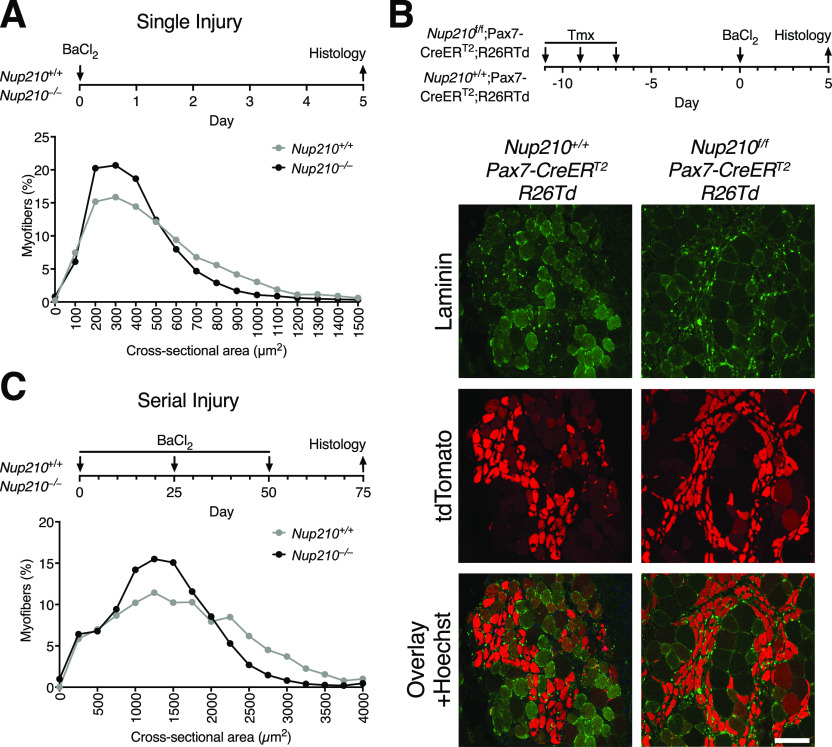
Figure 3. Nup210 ablation results in delayed muscle regeneration.
(A) Young (6–8 wk old) Nup210+/+ and Nup210−/− mice were subjected to BaCl2-induced muscle injury and muscle regeneration was analyzed 5 d later. Top: Schematic illustration of experimental approach. Bottom: Quantification of myofiber cross-sectional area distribution. n = 3, data are binned in 250 μm2 bins and are plotted as mean. (B) Nup210+/+/Pax7-CreERT2 and Nup210f/f/Pax7-CreERT2 mice carrying a Cre-inducible tdTomato reporter (R26Td) were treated with tamoxifen before being subjected to BaCl2 muscle injury. The tdTomato-positive myofibers were analyzed by immunofluorescence in muscle sections. Laminin was used as counterstain to detect muscle fibers. Top: Schematic representation of experimental approach. Bottom: Representative immunofluorescence images from TA sections. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) Young Nup210+/+ and Nup210−/− mice were subjected to BaCl2-induced serial muscle injury (three injuries total), and muscle regeneration was analyzed 25 d after last injury. Top: Schematic illustration of experimental approach. Bottom: Quantification of myofiber cross-sectional area distribution. n = 3, data are binned in 250-μm2 bins and are plotted as mean.