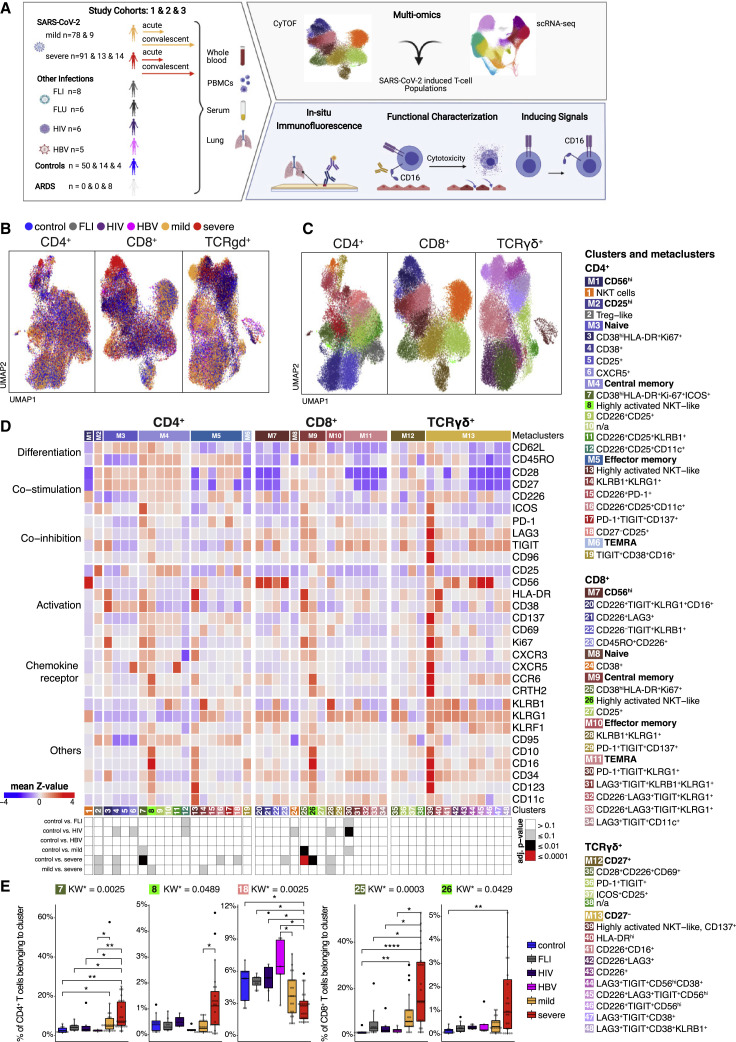
Figure 1.
Accumulation of HLA-DRhiCD38hi highly activated but also CD16 expressing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in severe COVID-19
(A) Overview of the study cohort and methodological pipeline. Samples were collected from mild and severe COVID-19 patients during the acute and convalescent phase enrolled in Berlin (cohort 1), Bonn (cohort 2), or Aachen (cohort 3), patients suffering from other acute respiratory infections (FLI, being chronically infected HIV, or HBV, patients with non-infectious ARDS as well as controls. CyTOF and scRNA-seq combined with VDJ-seq-based T cell clonotype identification were used to determine COVID-19 as well as severity-specific alterations in the T cell compartment. The obtained results together with serum proteomics and in situ immunofluorescence data were used to develop hypotheses on their functional properties and inducing mechanisms, which were tested in ex vivo cultures. Detailed sample information included in all reported assays can be found in Table S1.
(B and C) UMAPs generated of CD4+ (left), CD8+ (middle), and TCRgd+ (right) T cells from CyTOF. Cells are colored according to donor (B) or cluster (C) origin. For visualization purposes, each UMAP shows 30,000 cells.
(D) Heatmap of CyTOF data (covering CD4+ (left panel), CD8+ (middle panel), and TCRgd+ (right panel) T cells. Z score standardized staining intensity of each marker (rows) per cluster (1–48, in columns, lower part). Clusters were grouped into metaclusters, as defined by the numbers 1–13 (in columns, upper part). Significance levels of differential cluster frequency for the following groups: controls (n = 9), FLI (n = 8), HIV (n = 6), HBV (n = 5), mild acute COVID-19 (n = 28), and severe acute COVID-19 (n = 35). Kruskall-Wallis test and post hoc Dunn’s multiple comparison test. All combinations where tested, only comparisons with healthy controls are shown.
(E) Box plots of CD4+ (7, 8, 18) and CD8+ (25, 26) T cell clusters determined by CyTOF generated from controls (n = 9), FLI (n = 8), HIV (n = 6), HBV (n = 5), mild acute COVID-19 (n = 20), and severe acute COVID-19 (n = 23) patient samples. Kruskall-Wallis test and post hoc Dunn’s multiple comparison test. KW∗: adjusted p value (Benjamini-Hochberg) of a Kruskal-Wallis test. All combinations where tested, only comparisons with healthy controls are shown (∗p < 0.1, ∗∗p < 0.01,∗∗∗p < 0.001,∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).