Figure 2.
Single-cell transcriptomics of T cells during acute mild and severe COVID-19
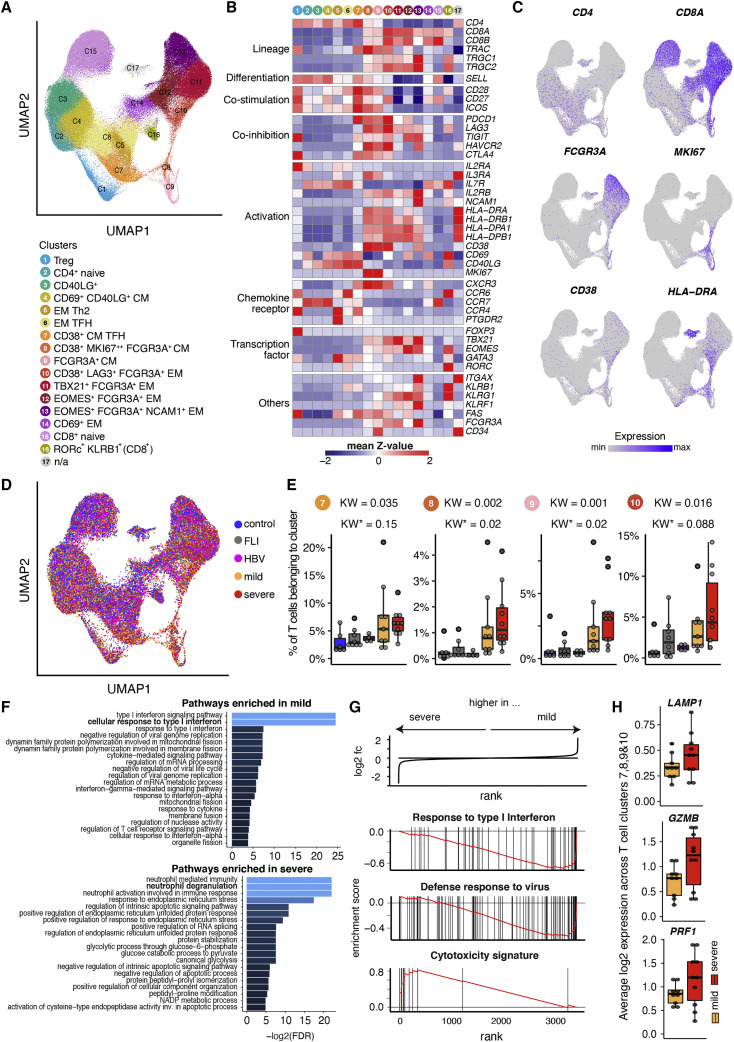
(A) UMAP of T cell clusters from controls (n = 6), FLI (n = 8), HBV (n = 4), mild COVID-19 (n = 9), and severe COVID-19 (n = 10) patients.
(B) Heatmap showing the Z score standardized gene expression (rows) per T cell cluster (columns).
(C and D) UMAPs as shown in (A) with superimposed CD4, CD8A, FCGR3A, MKI67, CD38, and HLA-DRA expression (C), with cells colored according to disease group origin. For visualization purposes, cells were downsampled to 10,000 cells per disease group.
(E) Box plots of a selection of scRNA-seq T cell clusters whose abundances are higher in both mild and severe COVID-19 compared with other severity groups (the analyzed number of patients are specified in the legend of ). KW, KW∗: raw and adjusted p value (Benjamini-Hochberg) of a Kruskal-Wallis test, respectively.
(F) Bar plot indicating the negative log2-transformed adjusted p value (Benjamini-Hochberg) of the 20 most significant enriched pathways that are (top) upregulated in mild COVID-19 acute phase, compared with severe COVID-19 acute phase, (bottom) vice versa. Pseudobulk gene expression was calculated per sample among scRNA-seq T cell clusters 7, 8, 9, and 10.
(G) Enrichment plots from GSEA performed on the ranked gene list of the comparison severe versus mild COVID-19. The graph shows the mapping of the signature genes on the ranked gene list. The curve corresponds to the running sum of the weighted enrichment score (ES). The ranked gene list was calculated from the normalized pseudobulk expression data of severe and mild COVID-19 acute phase among scRNA-seq T cell clusters 7, 8, 9, and 10.
(H) Box plots of the average log2-transformed expression among T cell clusters 7, 8, 9, and 10 from mild (n = 9) and severe (n = 10) COVID-19 acute samples, for three genes included in the cytotoxicity signature (LAMP1, GZMB, and PRF1).