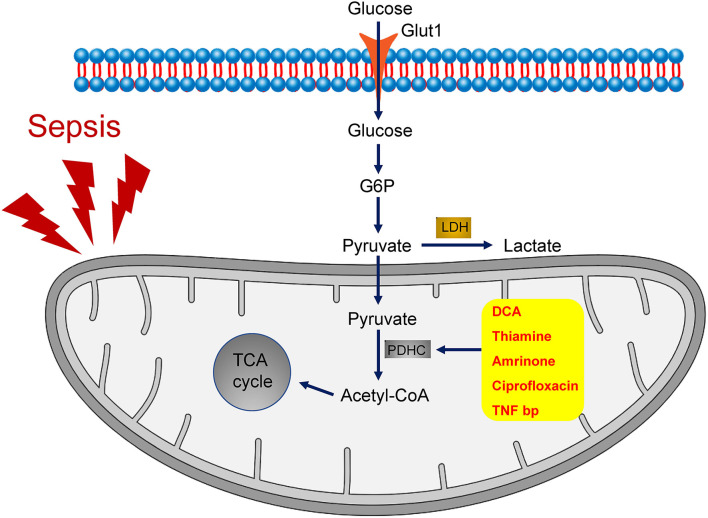
Figure 1.
The role of PDHC in the metabolism of sepsis. During the process of glycolysis, one molecule of glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate. Inactivation of PDHC results into anaerobic glycolysis, which is the primary metabolic pathway in sepsis. By contrast, activation of PDHC leads to pyruvate translocation to mitochondrial and the consequent acceleration of aerobic oxidation. A group of drugs that target PDHC activation, including dichloroacetate (DCA), thiamine, amrinone, ciprofloxacin, and TNF-binding protein (TNFbp), have been shown to ameliorate the symptoms of sepsis.