Figure 2. Berberine protected mice from cartilage damage in an AMPK-dependent manner in a post-traumatic OA model in mice.
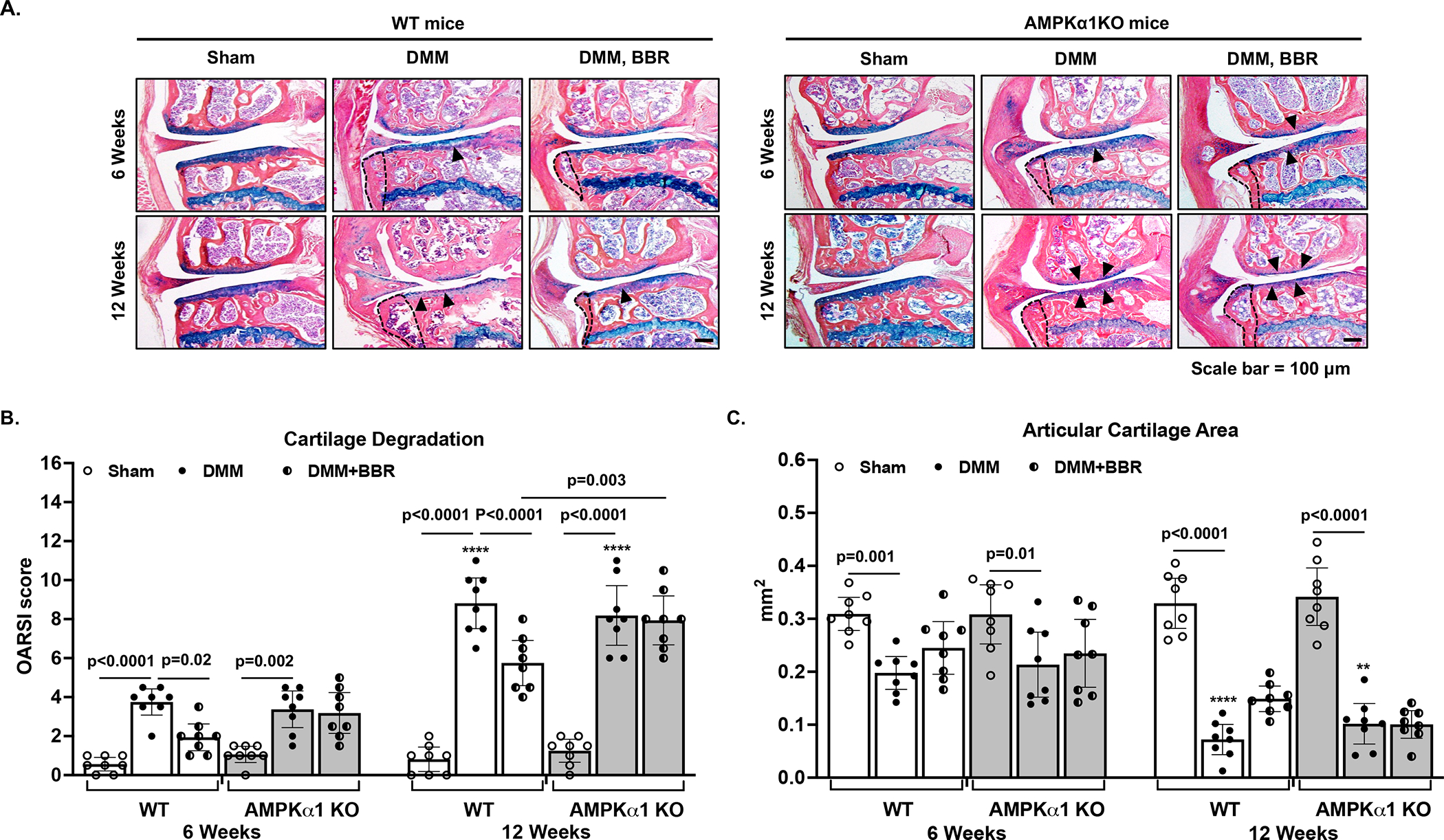
Both WT and AMPKα1 KO mice were subjected to the DMM surgery to induce OA development. Sham surgery was used as a control. Two weeks after the surgery, mice in the treatment group started to receive berberine chloride (BBR) via drinking water daily. At 6 and 12 weeks after the DMM surgery, mice were sacrificed and histological analysis of mouse knee sections (A) and assessment of cartilage damage (indicated by black arrowheads) including cartilage degradation (B) and cartilage area (C) were performed as described in the Methods (n=8 for each time point per group). Statistical analysis was performed using Two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (multiple comparisons between sham and DMM, sham and DMM+BBR, and DMM and DMM+BBR at each time point) in B and C. The data were expressed as mean with 95% CI. Only p values with significance were indicated in the figures. ****p<0.0001, **p<0.002, comparing with each respective condition at 6 weeks.
