Fig. 5: Activation-dependent TF partners influence Runx1 localization.
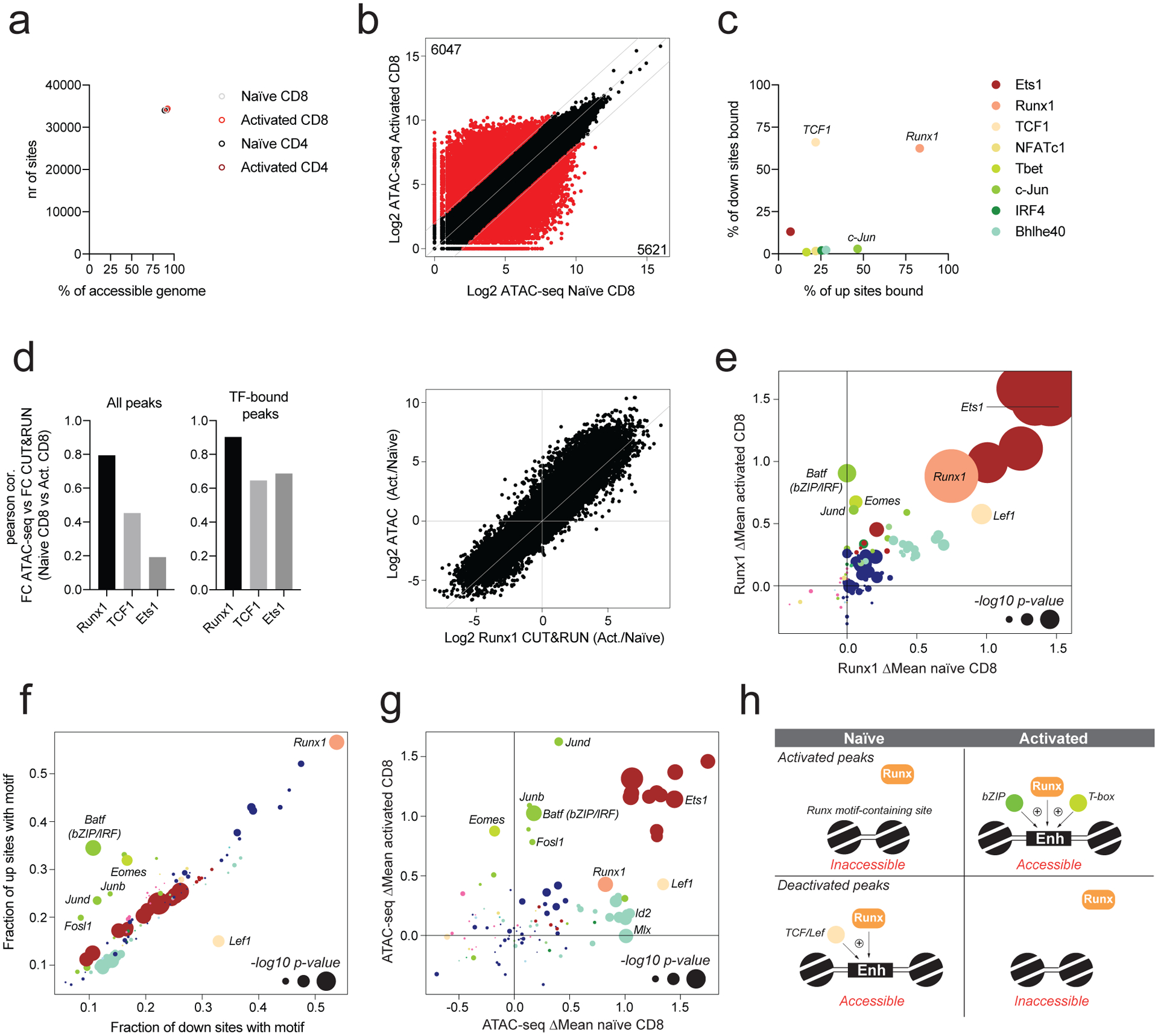
a: Runx1 binding was determined in naïve and activated CD4 and CD8 T cells using CUT&RUN. The number of ATAC-seq peaks bound by Runx1 is shown, together with the fraction of all accessible peaks (>100 ATAC-seq reads) that is bound by Runx1.
b: Chromatin accessibility in naïve and activated CD8 T cells across all ATAC-seq atlas peaks. Peaks with >4-fold differential accessibility are highlighted in red. Number of peaks with higher and lower chromatin accessibility in naïve and activated CD8 T cells is indicated.
c: Fraction of differentially accessible chromatin regions (highlighted in panel b) bound by each transcription factor.
d: Pearson correlation between changes in chromatin accessibility and changes in TF binding intensity for Runx1, TCF1, and Ets1 in activated vs naïve CD8 T cells. Analysis was done for all peaks or only the peaks bound by the respective TF. Scatter plot showing the fold change in Runx1 binding and fold change in chromatin accessibility in activated vs naïve CD8 T cells.
e: Effect of TF binding motif variation on Runx1 binding in naïve and activated CD8 T cells. Only peaks that were differentially accessible in naïve and activated CD8 T cells (panel b) were included in the analysis. Data points are colored by TF family and scaled according to the −log10 p-value of a two-sided t-test comparing allelic ratios between peaks with stronger motif matches on the B6 vs Cast allele. The most significant p-value obtained across the two cell types (naïve and activated CD8) was used for scaling.
f: TF-binding motif occurrence at peaks gaining (up sites) or losing accessibility (down sites) upon T cell activation. Motif significance of global allelic imbalance was calculated using two-sided t-test using the same approach as in Fig. 1e.
g: Effect of TF binding motif variation on chromatin accessibility in naïve and activated CD8 T cells. A two-sided t-test was used to calculate motif p-values as described in Fig. 1e. Only peaks that were differentially accessible in naïve and activated CD8 T cells (panel b) were included in the analysis.
h: Model of Runx1 activity at sites gaining or losing chromatin accessibility upon T cell activation.
