Fig. 7: Drivers of chromatin accessibility across T cell subpopulations.
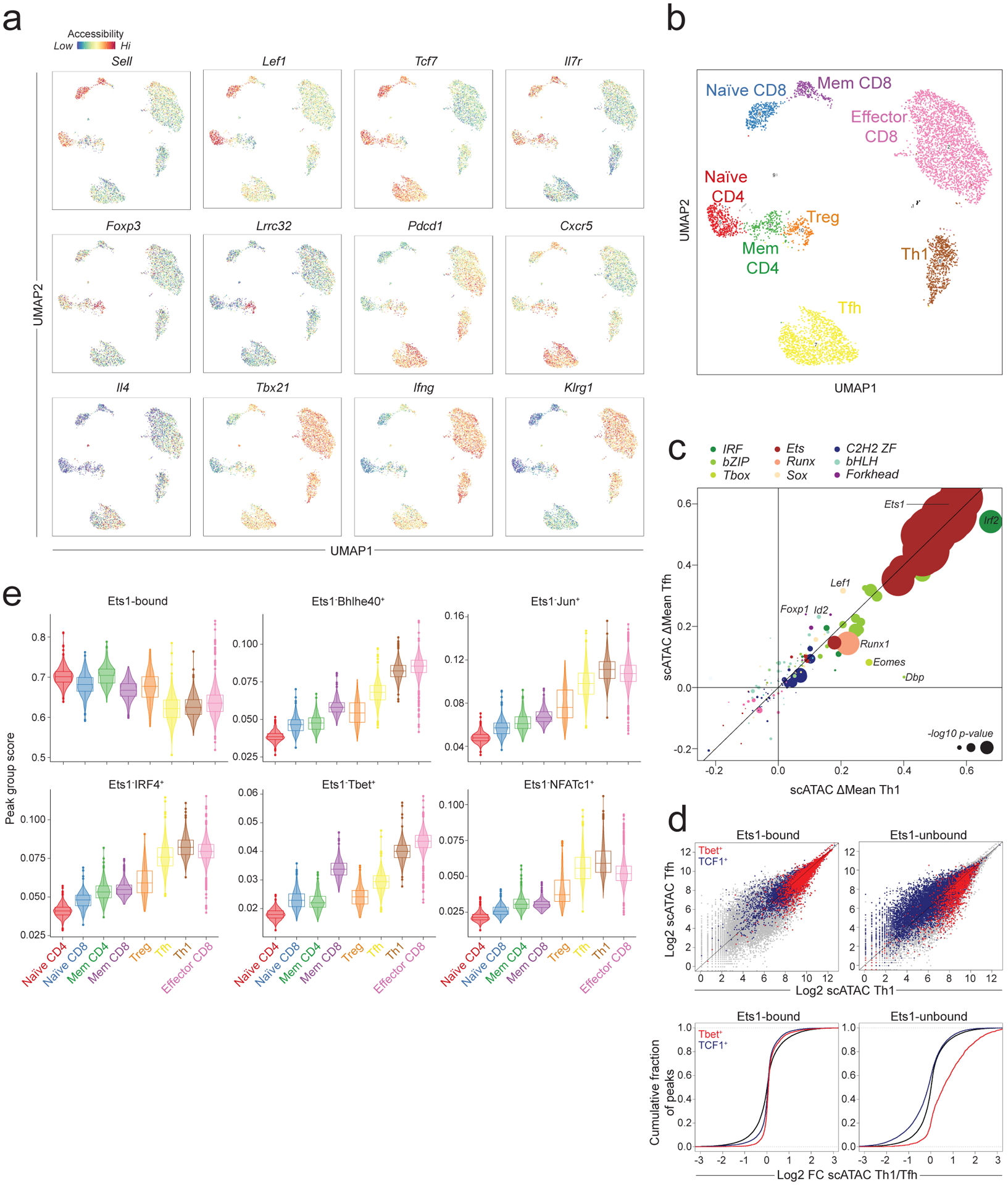
a: Chromatin accessibility at selected loci across T cell subpopulations in LCMV infected (B6/Cast) F1 mice measured by single cell (sc) ATAC-seq on total splenic CD4 and CD8 T cells (n=6043 cells).
b: Subset annotation.
c: Effect of genetic variation in TF binding motifs on allele-specific pseudo-bulk scATAC-seq counts in Th1 and Tfh cells. Data points are colored by TF family and scaled according to the −log10 p-value of a two-sided t-test comparing the allelic ratios between peaks with stronger matches on B6 vs Cast allele.
d: Pseudo-bulk scATAC-seq data showing accessibility in Th1 vs. Tfh cells at Ets1-bound or -unbound sites co-occupied by T-bet or by TCF1. Grey dots (top) and black lines (bottom) show all accessible peaks.
e: Violin plots and box plots showing accessibility of indicated peak groups across T cell subsets (n = 6043 cells). The center line in the box plots represents the median, the box limits represent the 25th and 75th percentiles, and the whiskers are the minimum/maximum values within 1.5 times the interquartile range. n = the number of cells in each cell annotation (420 Naïve CD4, 344 Naïve CD8, 234 Mem CD4, 231 Mem CD8, 198 Treg, 1321 Tfh, 652 Th1, 2583 Effector CD8).
