Extended Data Fig. 1. RNA-seq and ATAC-seq of naïve and activated CD4 and CD8 T cells.
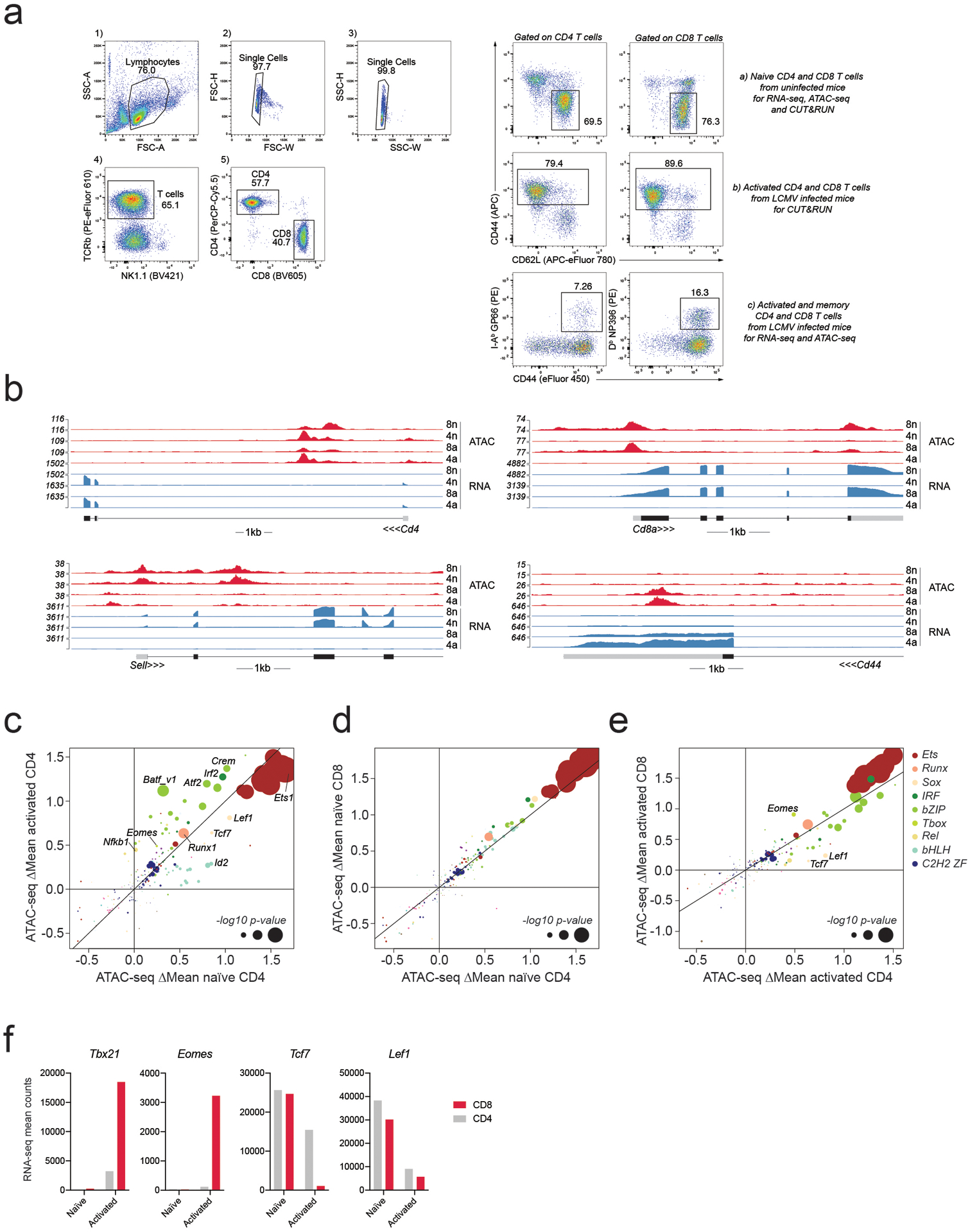
a: Example of gating strategy for cell isolation from the spleen. Live lymphocytes were identified based on FSC-A/SSC-A. Doublets were gated out and CD4 and CD8 T cells were identified as TCRβ+CD4+ and TCRβ+CD8+, respectively. Naïve CD4 and CD8 T cells used as input for RNA-seq, ATAC-seq, and CUT&RUN experiments were isolated from uninfected mice as CD44+CD62L− cells. Bulk activated CD4 and CD8 T cells used as input for CUT&RUN experiments were isolated as CD44+ cells from LCMV Armstrong infected mice on day 7–8 post-infection (p.i.). LCMV-specific activated and memory CD4 and CD8 T cells used as input for ATAC-seq and RNA-seq experiments were isolated based on tetramer staining on day 7 or day 60 p.i.
b: RNA-seq and ATAC-seq reads at the Cd4, Cd8a, Sell and Cd44 loci in naïve and activated CD4 and CD8 T cells.
c-e: Effect of TF binding motif variants on chromatin accessibility measured as ΔMean in naïve and activated CD4 T cells (A), naïve CD4 and CD8 T cells (B), activated CD4 and CD8 T cells (C). Data points are colored by TF family and scaled according to the −log10 p-value of a two-sided t-test comparing the mean allelic ratios between peaks with stronger matches on the B6 vs Cast allele. The most significant p-value obtained across the two cell types (naïve and activated CD8) was used for scaling. Motifs with <50 variant-containing motif occurrences were excluded from the plot.
f: Mean RNA-seq counts for Tbx21, Eomes, Tcf7 and Lef1 in naïve and activated CD4 and CD8 T cells.
