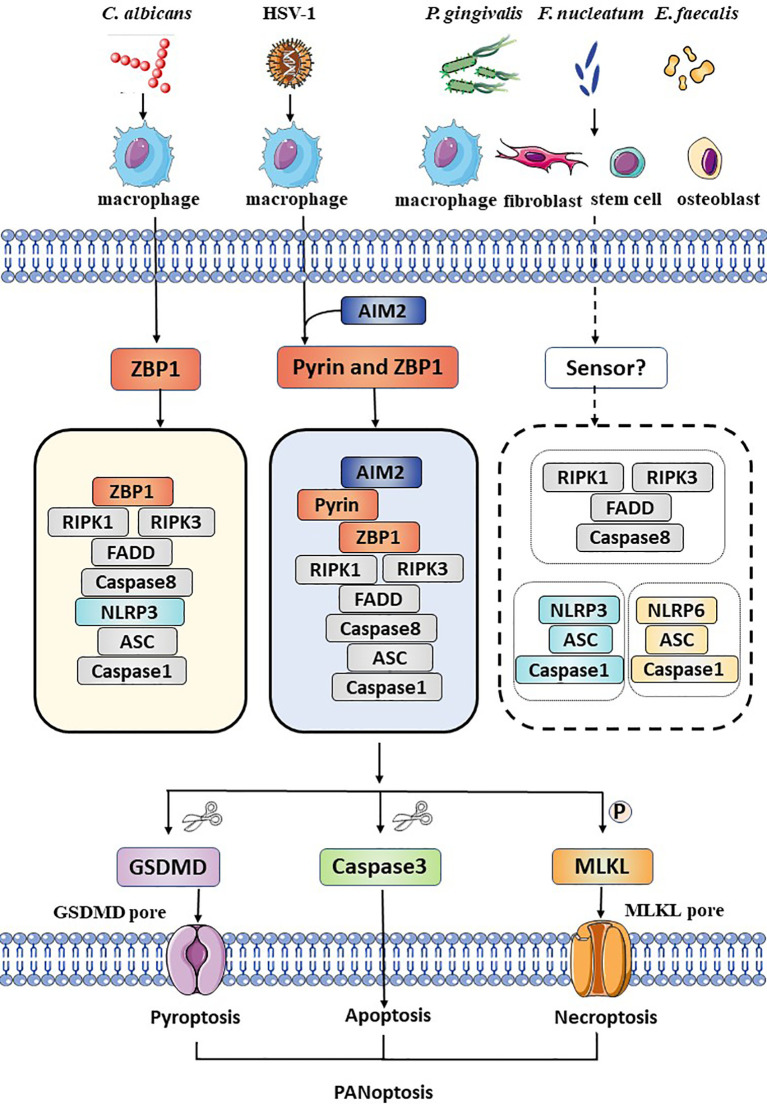
Figure 1.
Schematic summary of the activation of PANoptosis in several kinds of cells during oral pathogens infection. During Candida albicans infection, ZBP1 senses the pathogen and recruits RIPK3, RIPK1, and caspase-8 to assemble the ZBP1 PANoptosome, causing GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis, caspase-8-dependent apoptosis and MLKL-mediated necroptosis (PANoptosis). DNA virus, HSV-1, is sensed by ZBP1 and pyrin and actives the AIM2 PANoptosome which inducing PANoptosis in macrophages. Bacteria such as Porphyromonas gingivalis, Fusobacterium nucleatum, and Enterococcus faecalis active pyroptosis, apoptosis, necroptosis and release intracellular cytokines and DAMPs not only in immune cells, but also in fibroblasts, stem cells and osteoblasts. However, the exact sensor is unclear. The NLRP3 inflammasome, the NLRP6 inflammasome and the necroptosome are involved, but the interaction among these molecules remains unknown.