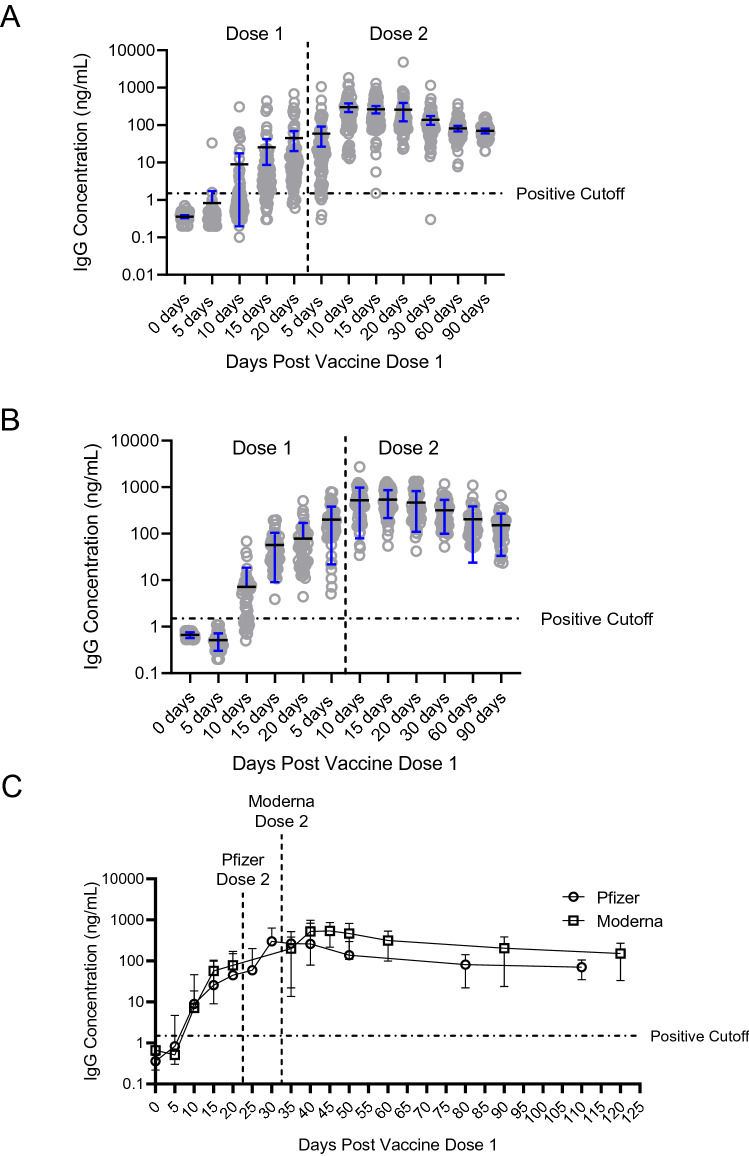
Figure 1.
SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody time course trajectories of participants receiving either Pfizer or Moderna vaccines were largely similar. (A) Relative quantification of SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies in participants who received the Moderna vaccine (N = 51) reveal increasing concentration in the days following the first and second dose. The average antibody concentration of participants prior to receiving vaccination was 0.66 ± 0.09 ng/mL while 90 days after vaccination this number stabilized at 151.7 ± 118.5 ng/mL. (B) Similarly, antibody concentration increased following vaccination by the Pfizer vaccine (N = 79). The average antibody concentration of participants prior to receiving vaccination was 0.35 ± 0.14 ng/mL while 90 days after vaccination this number stabilized at 70.32 ± 35.42 ng/mL. (C) Time courses of antibody development are well-aligned across the two vaccines.