FIGURE 1.
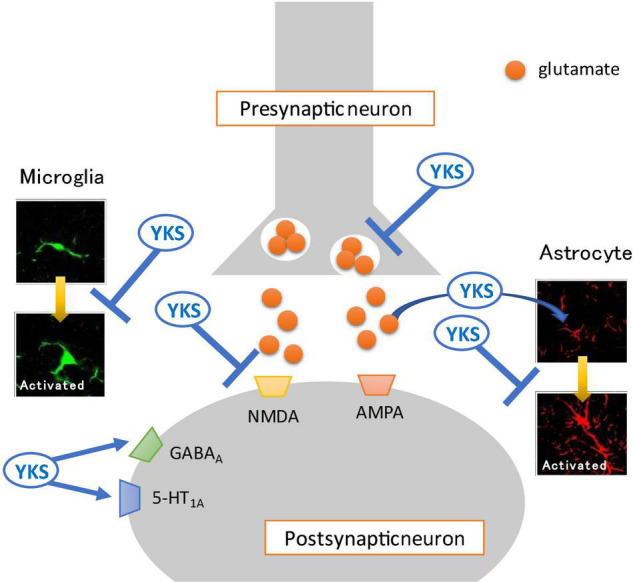
Mechanisms of action of Yokukansan for neuropathic pain. Several different mechanisms of action may act on neurotransmission in the spinal dorsal horn. (1) Attenuation of excessive glutamate release from presynaptic neurons. (2) Promotion of the uptake of glutamate into astrocytes. (3) Antagonistic effect on the glutamate receptor, N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. (4) Agonistic effect on the GABAA receptor. (5) Inhibition of the activation of glia cells (microglia and astrocyte). (6) Agonistic effect on the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor. YKS, Yokukansan; AMPA, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor.
